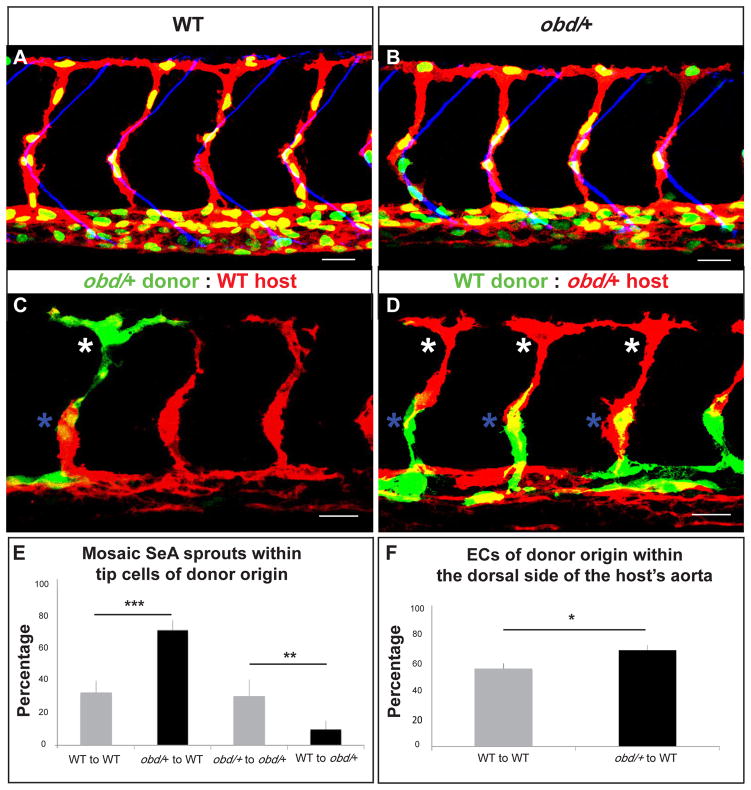
Figure 2. ECs with less Sema-PlxnD1 signaling tend to become tip cells and occupy the aorta’s dorsal side.
(A–B) 32 hpf vasculatures. EC nuclei (green), membranes (red). SBs, blue. (A) WT. (B) obd/+. (C–D) 28 hpf vasculatures with ECs of donor (green) and host (red) origin. Asterisks: Tip cells (white), stalk cells (blue). (E) Percentage of mosaic SeAs with tip cells of donor origin in homogenotypic (grey bars) and heterogenotypic (black bars) chimeras. (F) Percentage of ECs of donor origin found within the dorsal side of the host’s arterial tree in homogenotypic (grey bar) and heterogenotypic (black bar) chimeras. (E–F) *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Error bars, s.e.m. (E) n = 27 WT to obd/+, n = 18 obd/+ to obd/+, n = 38 obd/+ to WT, n = 34 WT to WT. Error bars, s.e.m. (F) n = 24 WT to WT, n = 32 obd/+ to WT. (A–D) Anterior, left; dorsal, up. Scale bars, 30 μm. See Figure S2 and Movie S1.