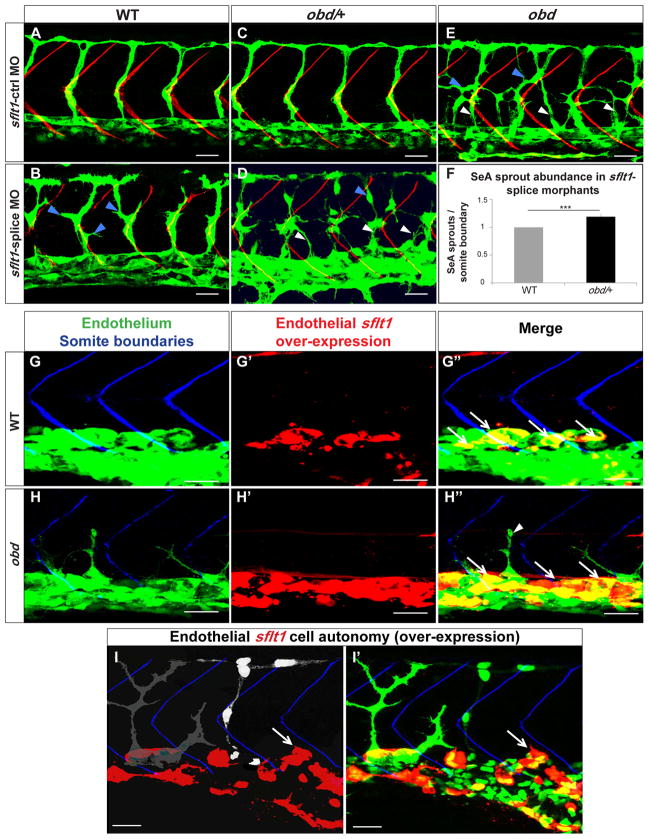
Figure 4. plxnD1 and sflt1 interact genetically, sflt1 limits SeA angiogenesis cell autonomously.
(A–I) 32 hpf trunk vasculatures, green. (A–E) SBs, red. White arrowheads, ectopic SeA sprouts. Blue arrowheads, ectopic SeA branching. (A, C, E) Embryos treated with 20 ng of sflt1-ctrl MO: WT (A), obd/+ (C), obd (E). Embryos treated with 20 ng of sflt1-splice MO: WT (B), obd/+ (D). (F) 23 hpf SeA sprout abundance in WT (left, grey bar) and obd/+ (right, black bar) sflt1-splice morphants. n = 20 WT and n = 19 obd/+. Error bars, s.e.m. ***p < 0.001. (G–I′) SBs, blue. GAL4FF/UAS-mediated endothelial-specific sflt1 over-expression, red. White arrows, missing SeA sprouts. (G′–H″) Endothelial sflt1 over-expression inhibits SeA sprouting. WT (G-G″). obd (H-H″), note lack of sflt1 over-expression (red) in remaining SeA sprout (white arrowhead). (I-I′) Mosaic vasculature with ECs from both obd donor and WT host. Endothelial-specific and mosaic sflt1 and DsRed co-expression restricted to the WT endothelium (red, I-I′). obd ECs express cytosolically-targeted EGFP (grey in I; green in I′). WT ECs express nuclear-targeted EGFP (white in I; green in I′). obd and WT ECs without sflt1 over-expression (DsRed-) from SeA sprouts even next to sflt1 over-expressing WT ECs (DsRed+). WT ECs over-expressing sflt1 (DsRed+) fail to form SeA sprouts (white arrows, I-I′). (G-H″) n = 30 embryos with over-expression per genotype, all showing suppression of SeA sprouting. Anterior, left; dorsal, up. Scale bars, 30 μm. See Figure S4.