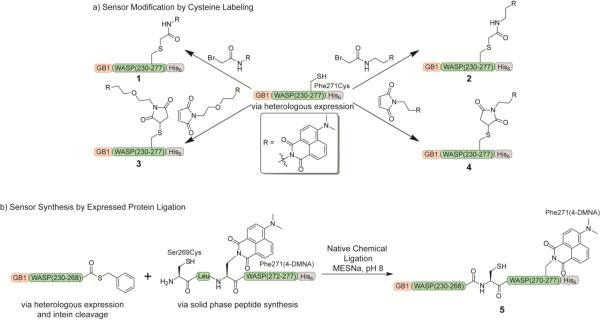
Figure 2.
Approaches for the synthesis of 4-DMN-labeled Cdc42 sensors. a) Generation of the sensor by cysteine labeling with 4-DMN-modified α-bromoacetamides and maleimides. The GB1-WASP-His6 protein was obtained through heterologous expression in E. coli, and Cys271 was labeled with 4-DMN reagents of varying linker length. b) Incorporation of the 4-DMN amino acid into the sensor through expressed protein ligation. The N-terminal portion of the sensor was expressed in E. coli as a fusion to an intein, allowing cleavage with sodium 2-mercaptoethanesulfonate (MESNa) to yield the corresponding thioester, and a peptide containing the 4-DMNA amino acid was generated by Fmoc-based solid phase peptide synthesis. Reaction of the recombinant and peptide fragments in the native chemical ligation reaction yielded the full-length sensor.