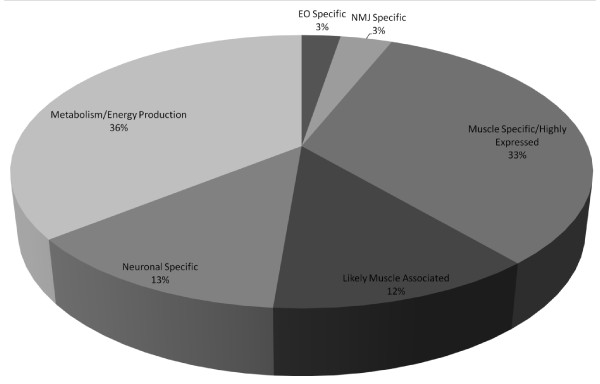
Figure 3.
Classification of proteins identified in electric organ fractions by tissue association or function as determined by UniProtKB annotation. Electric organ fractions were separated one dimensionally and analyzed by nanospray electrospray ionization quadrupole linear ion-trap tandem mass spectrometry (ESI-LTQ MS/MS). Mass spectral matching of raw spectra against UniProtKB and Torpedo cDNA library was performed in BioWorks 3.3.1 in which the peptide acceptance criteria was set at ΔCn >0.1, a variable threshold of Xcorr versus charge state: Xcorr = 1.9 for z = 1, Xcorr = 2.2 for z = 2, and Xcorr = 2.5 for z = 3, protein Xcorr >40, and a peptide probability based score with a P value <0.01. All cDNA sequences were queried in blastx (standard genetic code, Swiss-Prot, default algorithm parameters except for BLOSSUM80 scoring matrix) for identification via sequence similarity with a known protein, first across all species and then against Homo sapiens selected database. Cytosolic proteins were separated two dimensionally, analyzed via matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization - time of flight/time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF/TOF MS), and identified by MASCOT. Identification criteria was set at a protein score CI >95%, protein score >69, and proteins with isoelectric points (PI) and molecular weights (MW) that match the gel spot. Each identification was queried in UniProtKB for annotation of tissue expression and or function then categorized by the sections composing the pie chart. (See Additional file 3 for a list of proteins composing the pie chart.)