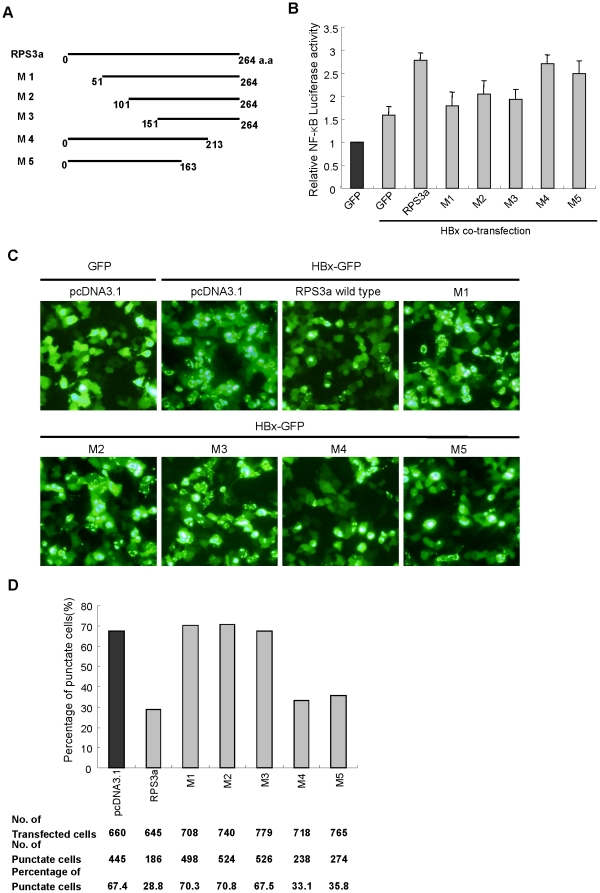
Figure 6. The N-terminal domain of RPS3a is critical for NF-κB hyperactivation and the soluble expression of HBx.
(A) Construction of RPS3a deletion mutants. (B) The N-terminal domain of RPS3a is responsible for HBx-induced NF-κB activity. After co-transfection with wild-type or deletion mutants of RPS3a (0.4 µg) and pEG-HBx (0.4 µg) in Huh7 cells, the relative NF-κB activity was measured. (C) The N-terminal region of RPS3a is responsible for the punctate expression of HBx. After 36 hr co-transfection with pEG-HBx-GFP (2 µg) and wild-type or mutant RPS3a (2 µg), the expression pattern of HBx-GFP protein was examined by fluorescence microscopy (magnification ×200). (D) Number of cells showing punctate expression was counted under fluorescence microscopy. Ratio of punctate cells was calculated and presented by bar graph.