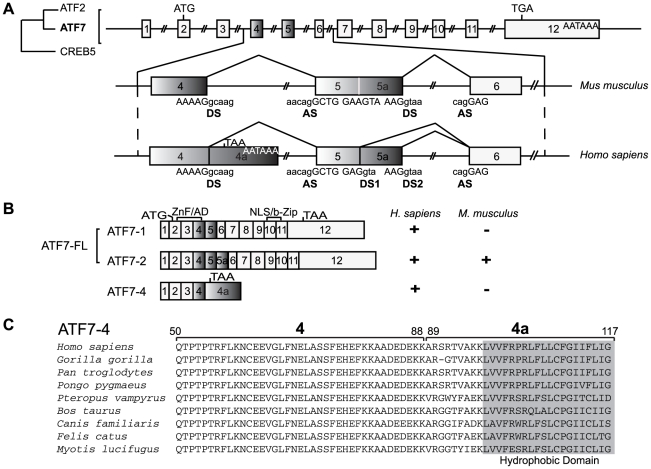
Figure 1. Identification of ATF7-4 as a novel alternatively spliced ATF7 isoform.
(A) The structure of the ATF7 gene, a member of the ATF2/ATF7/CREB5 family, is shown schematically: the twelve exons are indicated by numbered boxes, and an alternative splicing region encompassing exons 4 to 6 is compared between human and mouse species. The sequences of the donor (DS) and acceptor (AS) sites for splicing are indicated, capital and small letters corresponding to the exonic and the intronic parts respectively. 4a and 5a are alternatively included exons adjacent to exons 4 and 5 respectively. The start codon, stop codons and polyadenylation sites are shown. (B) Schematic representation of the exonic structure of three ATF7 alternatively spliced isoforms. The regions encoding the zinc finger (ZnF)/activation domain (AD) or the nuclear localization signal (NLS)/basic region-leucine zipper (b-Zip) are indicated. “+” indicates that the proteins are encoded, either in human or in mouse species. (C) Amino acid sequence alignment of ATF7-4 exon 4 and specific exon 4a of a series of mammalian species. A conserved C-terminal hydrophobic domain is highlighted.