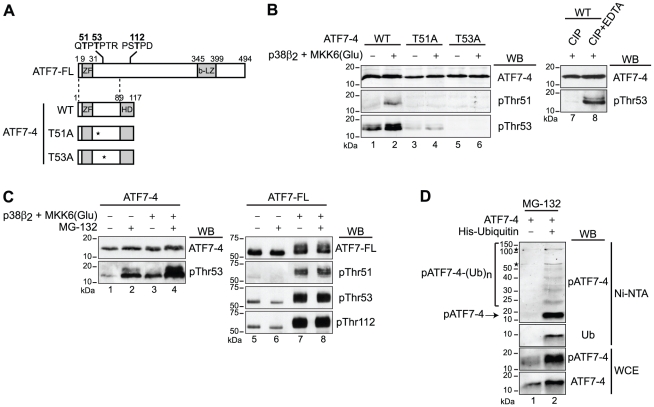
Figure 4. ATF7-4 is phosphorylated and subjected to degradation by a proteasome 26S-dependent pathway.
(A) Schematic diagrams indicating the known phosphorylated residues of ATF7-FL protein and the derived series of ATF7-4 mutants used. (B) The indicated WT or mutant versions of ATF7-4 were co-expressed with p38β2 and constitutively active MKK6(Glu) in HeLa cells. Cell lysates were either untreated or treated with calf intestinal phosphatase (CIP), in presence of EDTA where indicated. The analysis was performed by western-blotting (WB) with specific antibodies as specified to detect non-phosphorylated (ATF7-4) and phosphorylated ATF7-4, either on residues Thr51 (pThr51) or Thr53 (pThr53). (C) ATF7-4 (lanes 1–4) and ATF7-FL (lanes 5–8) were co-expressed with p38β2 and MKK6(Glu) in HeLa cells treated with MG-132 proteasome inhibitor as indicated. Cell lysates were analyzed by WB with specific antibodies to detect ATF7-4, ATF7-FL and their phosphorylated forms. (D) ATF7-4 was co-expressed with 6His-Ubiquitin in HeLa cells treated overnight with MG-132. Whole cell extracts (WCE) were purified by a nickel affinity pulldown (Ni-NTA) and analyzed by WB with specific antibodies to detect the poly-ubiquitinated forms of ATF7-4. The asterisks indicate nonspecific signal.