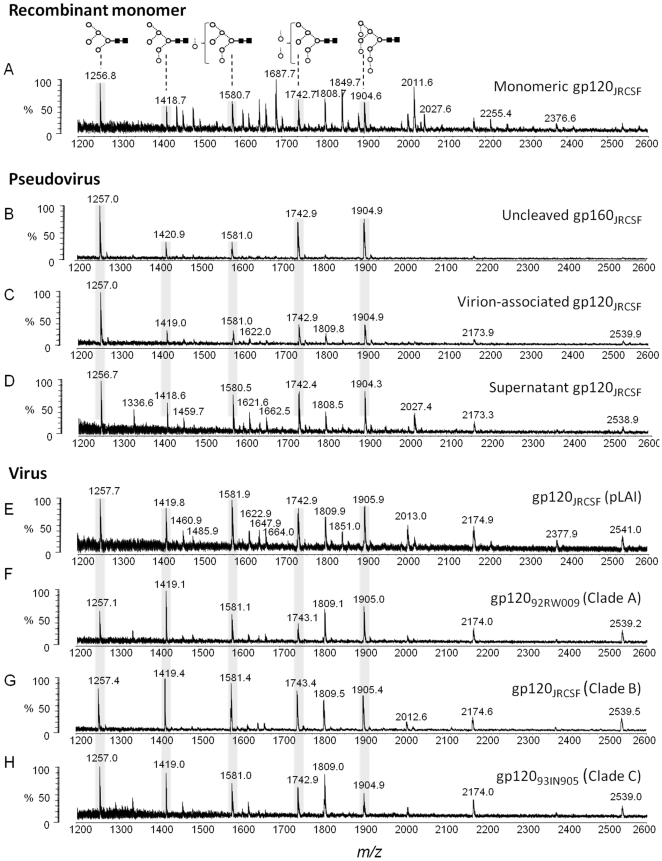
Figure 1. Comparison of recombinant, pseudoviral and viral gp120.
MALDI-TOF MS analyses of released desialylated N-linked glycans ([M+Na]+ ions) from: (A) recombinant monomeric gp120JRCSF expressed in HEK 293T cells; (B, C and D) respectively gp160JRCSF, gp120JRCSF and soluble, non-virion associated envelope gp120JRCSF isolated from pseudoviral particle preparations generated by transfection of HEK 293T cells with the pSVIII-JRCSF and pSG3Δenv plasmids at a ratio of 1∶10; (E) gp120JRCSF isolated from replication competent viral particles generated by transfection of HEK 293T cells with pLAI-JRCSF env molecular clone; (F, G and H) respectively gp12092RW009, gp120JRCSF and gp12093IN905 isolated from virus obtained by infection of human PBMCs. Symbols used for the structural formulae in this and subsequent figures: ⋄ = Gal, ▪ = GlcNAc, ○ = Man,  = Fuc [46]. The linkage position is shown by the angle of the lines linking the sugar residues (vertical line = 2-link, forward slash = 3-link, horizontal line = 4-link, back slash = 6-link). Anomericity is indicated by full lines for β-bonds and broken lines for α-bonds [46]. The oligomannose series are highlighted.
= Fuc [46]. The linkage position is shown by the angle of the lines linking the sugar residues (vertical line = 2-link, forward slash = 3-link, horizontal line = 4-link, back slash = 6-link). Anomericity is indicated by full lines for β-bonds and broken lines for α-bonds [46]. The oligomannose series are highlighted.