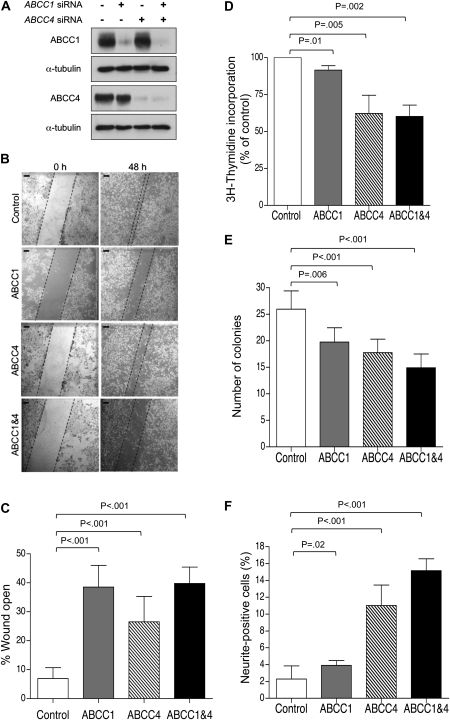
Figure 2.
Impact of ABCC1 and ABCC4 suppression in BE(2)-C human neuroblastoma cells. A) Western blot analysis of ABCC1 and ABCC4 protein expression following exposure of BE(2)-C cells to ABCC1- and ABCC4-specific siRNA molecules, alone or in combination, or to control siRNA (lane 1). B) Representative images of wound closure assay; Scale bar = 125 μm. C) Quantification demonstrating impaired motility of BE(2)-C cells depleted of ABCC1, ABCC4, or both, as measured by wound closure assay for 48 hours. D) 3H-thymidine incorporation assay in BE(2)-C cells depleted of ABCC1, ABCC4, or both. E) Clonogenic capacity of BE(2)-C cells upon depletion of ABCC1 and ABCC4 was assayed after 10 days. F) Neurite extension in BE(2)-C cells upon depletion of ABCC1 and ABCC4. In panels (C), (E), and (F), P values were derived from two-sided Student t test vs control, whereas one-sample t test (H0, μ = 100%) was used in panel (D). Means are derived from at least three independent experiments. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals. ABCC = ATP-binding cassette, subfamily C; siRNA = short interfering RNA.