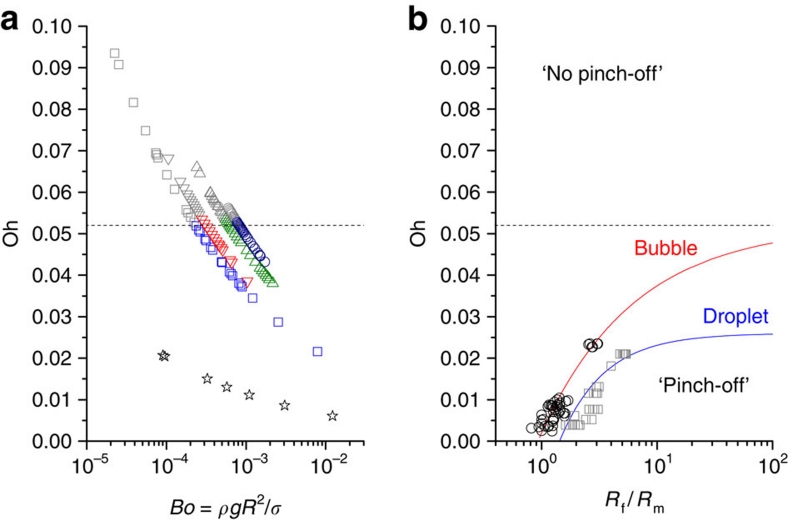
Figure 4. Phase diagram for jet formation from bursting bubbles.
(a) Experimental results for a wide range (20 μm<R<300 μm) of bubble sizes in water (star), ethanol (square), dodecane (downward triangle), decalin (upward triangle) and tridecane (circle) plotted in a phase diagram in terms of the Ohnesorge (Oh, for the capillarity effects) and Bond numbers (Bo, for the buoyancy effects). The zone of Oh<Oh* describes jetting cases, whereas the zone of Oh>Oh* indicates the absence of jetting. The critical Ohnesorge number is marked at Oh*≈0.052±0.005 (marked by the dashed line) for negligible buoyancy effects (at Bo<10−3). (b) General coalescence phase diagram in terms of the parent size ratio, Rf/Rm (Rf>Rm). Typical droplet–droplet (squares, ref. 30) and bubble–bubble (circles, ref. 31) systems show similar size ratio dependences of Oh*, below which pinching-off (or jetting) occurs. The droplet coalescence reaches the asymptote of Oh∞*=0.026 (ref. 28) for Rf=∞ or a droplet on a flat liquid surface. The asymptote for bubble is suggested to be around Oh∞*=0.052 (dashed line). The parent size ratio dependences of Oh* are fitted by an asymptotic function of Oh*=Oh∞*−a(Rf/Rm)−b with Oh∞*=0.052 (this paper), a=0.050, and b=0.535 for bubble and with Oh∞*=0.026 (ref. 28), a=0.039, and b=1.128 for droplet (solid lines).