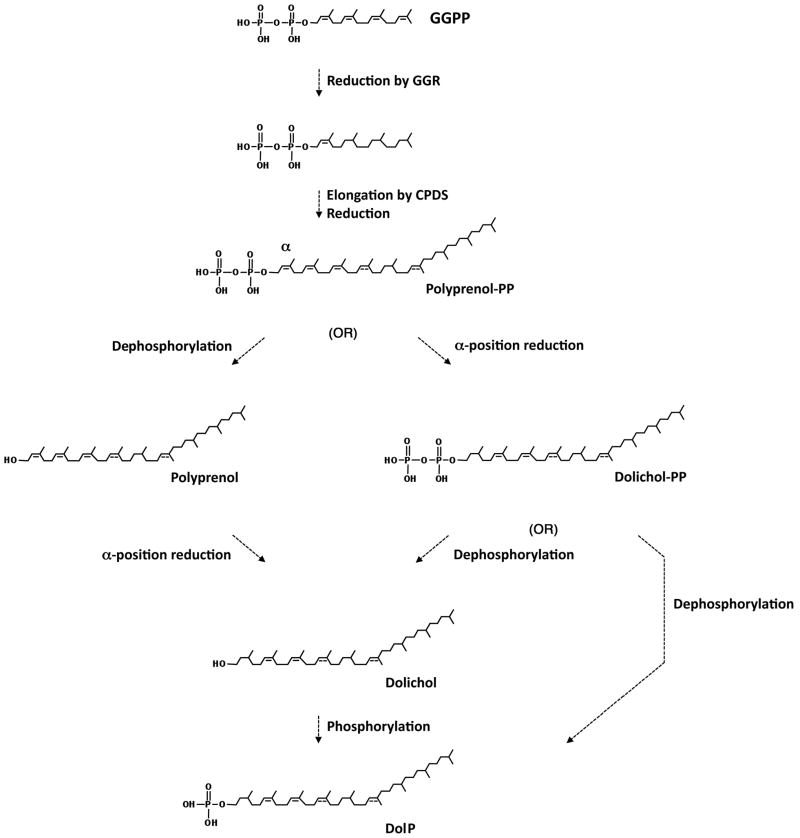
Fig 7.
A proposed S. acidocaldarius DolP biosynthesis pathway. In S. acidocaldarius, three IPP subunits and DMAPP, all synthesized via the classic MVA pathway [34], combine to form GGPP (not shown). Three of the four double bonds in this species are reduced by GGR; the α-position isoprene subunit remains unsaturated [36]. Four-six isoprene subunits are then added at the α-position of the GGPP backbone by cis-polyprenyl diphosphate synthase(s) (CPDS) [35] to generate C40, C45 and C50 polyprenol diphosphate (Polyprenol PP). The polyprenol diphosphate αposition isoprene subunit is indicated. At this point, removal of the two phosphate groups, followed by multiple reduction reactions and phosphorylation may occur to yield DolP, in a process reminiscent of what is proposed to occur in Eukarya [1,2]. Alternatively, C40, C45 and C50 polyprenol diphosphate may undergo multiple reduction reactions followed by removal of one phosphate group or removal of both phosphate groups and re-phosphorylation, in both cases yielding DolP. The order in which the α-position and other isoprene subunits of the polyprenol diphosphate precursor are reduced is not known. Furthermore, where the position of a double bond is only speculated, a dotted line is drawn.