Figure 9.
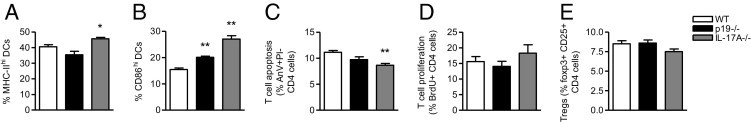
The effect of IL-17A or IL-23p19 deficiency on DCs and CD4+ T-cell responses. DC activation was increased by the lack of IL-23p19 and, to a greater extent, IL-17A, as shown by the proportion of DCs in the spleen expressing major histocompatibility complex class II (A) and CD86 (B) 6 days after anti-GBM globulin injection. C: Compared with WT animals, IL-17A−/− mice had decreased CD4+ T-cell apoptosis, whereas a trend toward reduced apoptosis was observed in IL-23p19−/− mice. CD4+ T-cell proliferation (D) and the proportion of Tregs (E) were not significantly affected by IL-23p19 or IL-17A deficiency. AnV, Annexin V; BrdU, bromodeoxyuridine; MHC-II, major histocompatibility complex class II; PI, propidium iodide; Tregs, regulatory T cells. *P < 0.05 versus WT; **P < 0.01 versus WT.
