Figure 5.
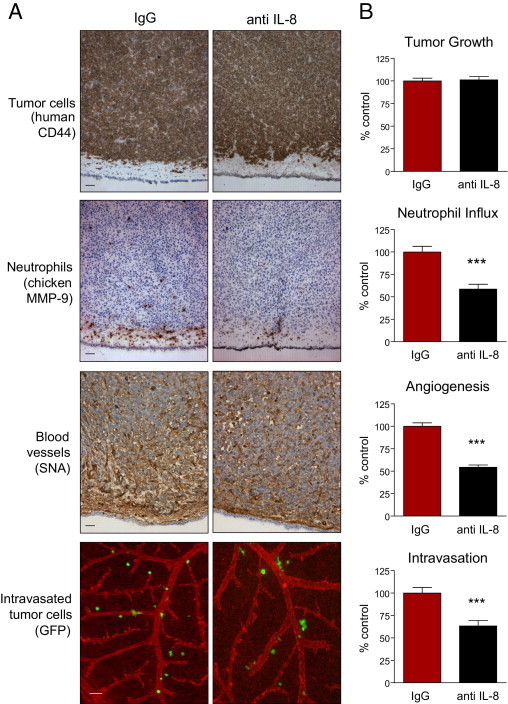
Specific inhibition of neutrophil influx into HT-hi/diss primary tumors coordinately diminishes tumor angiogenesis and tumor cell intravasation. HT-hi/diss primary tumors were treated with 20 μg control IgG or IL-8/CXCL8-neutralizing antibody (anti–IL-8) in five independent experiments. A: Immunohistochemical analysis of primary tumors. Sections from four to six individual tumors were stained with anti-human CD44 to discriminate human tumor cells (brown), anti-chicken MMP-9 antibody to visualize MMP-9–positive neutrophils (brown), and SNA to highlight blood vessels (brown). Intravasated GFP-tagged HT-hi/diss cells (green) were visualized using live cell imaging in the CAM in which blood vessels were highlighted by red fluorescent LCA. Scale bars = 50 μm. B: Tumor growth, neutrophil influx, tumor angiogenesis, and intravasation were quantified as described in Materials and Methods. Sixty-one and 47 tumor-bearing embryos were analyzed in control IgG- and anti IL-8–treated groups, respectively. Data are expressed as a percentage of IgG control and represent mean ± SEM. ***P < 0.001, two-tailed Student's t-test.
