Figure 7.
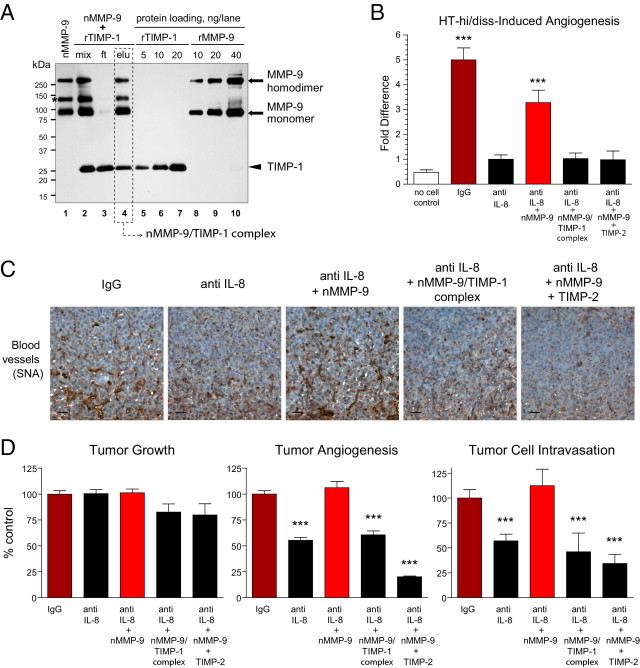
Rescue of diminished tumor angiogenesis and tumor cell intravasation via delivery of exogenous TIMP-free neutrophil proMMP-9. A: Generation of neutrophil proMMP-9–TIMP-1 complex. Neutrophils isolated from human peripheral blood were induced to release their MMP-9-containing secretory granules, and their proMMP-9 was purified using affinity chromatography (nMMP-9, lane 1). To generate the neutrophil proMMP-9–TIMP-1 complex, purified neutrophil proMMP-9 was mixed with recombinant human TIMP-1 (rTIMP-1) at 1:4 molar ratio (mix, lane 2). After incubation for 1 hour at ambient temperature, the protein mixture (mix) was applied to gelatin Sepharose beads to recover the formed proMMP-9–TIMP-1 complex (elu, lane 4) and remove excess TIMP-1 in the flow-through fraction (ft, lane 3). The proteins were separated using SDS-PAGE under nonreducing conditions, and Western immunoblot analysis was performed using a mixture of mouse anti-human MMP-9 and anti–TIMP-1 mAbs. Lanes 5–7 and 8–10: Loading controls for recombinant TIMP-1 and recombinant proMMP-9, respectively (nanograms per lane). The positions of molecular weight standards are indicated in kilodaltons on the left. Asterisk indicates the position of a 125-kDa heterodimer between proMMP-9 and NGAL (neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin), unique to neutrophils. The molar amounts of proMMP-9 (92 kDa) and TIMP-1 (28 kDa) eluted from gelatin Sepharose beads (dashed box) were calculated via comparison with corresponding protein loading controls and indicated a 1:1 stoichiometric complex between proMMP-9 and TIMP-1. B: Angiogenic and rescuing potential of neutrophil MMP-9 in the chick embryo collagen onplant model. HT-hi/diss cells were incorporated into 3D collagen onplants at 1 × 106 cells/mL with 3 μg/mL normal IgG or IL-8/CXCL8-neutralizing antibody (anti IL-8). Control onplants contained collagen only (no cell control). A subset of the HT-hi/diss–containing collagen onplants treated with anti IL-8 were additionally supplemented with 2 ng purified neutrophil proMMP-9 (nMMP-9) or a stoichiometric 1:1 molar complex between neutrophil proMMP-9 and TIMP1 corresponding to 2 ng nMMP-9 (nMMP-9–TIMP-1) or 2 ng neutrophil proMMP-9 mixed with 5 ng TIMP-2 (eightfold molar excess over nMMP-9). In two independent experiments, 22 to 42 individual onplants were analyzed in each group. Data are expressed as fold difference ± SEM calculated over angiogenesis levels in the anti IL-8 group. ***P < 0.001, two-tailed Student's t-test. C and D: Angiogenic and rescuing capacity of neutrophil MMP-9 in the chick embryo spontaneous metastasis model. HT-hi/diss primary tumors, developing on the CAM, were treated with control IgG or IL-8/CXCL8 neutralizing antibody (anti IL-8) in three independent experiments. A subset of anti-IL-8–treated tumors were additionally supplemented with 30 ng nMMP-9, purified nMMP-9/TIMP-1 stoichiometric complex corresponding to 30 ng nMMP-9, or a mixture of 30 ng nMMP-9 and 70 ng TIMP-2 (7.7-fold molar excess over nMMP-9). C: Immunohistochemical analysis of angiogenesis in primary tumors was performed on tissue sections stained with SNA to highlight blood vessels (brown). Scale bars = 25 μm. D: Tumor growth, angiogenesis, and intravasation were quantified in three independent experiments involving up to 45 tumor-bearing embryos for each treatment condition. Data are expressed as a percentage of IgG control and represent mean ± SEM. ***P < 0.001, two-tailed Student's t-test.
