Figure 3.
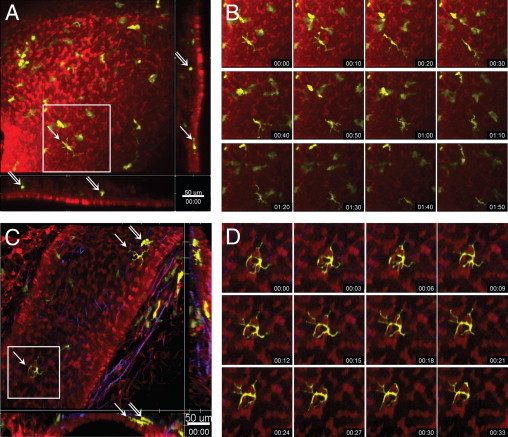
Steady-state motility of DCs within different layers of the airway mucosa. Two-photon microscopic images of the airway mucosa in central, large-diameter bronchi (A and B) or peripheral, small-diameter bronchi (C and D) with CD11c-EYFP+ DCs (yellow) located within and beneath the epithelium (red), revealed by SNARF-1 staining. Second harmonic signals generated by collagen fibers are shown in blue. A and C: Maximum-intensity projections along the Z-axis (top view) or the x- and y-axes (side views, representing only a few optical sections). Arrows indicate intraepithelial DCs with typical dendritiform morphologic characteristics; double arrows show subepithelial DCs with rounded or amoeboid shape. Scale bar = 50 μm. B and D: Image sequences (see Supplemental Videos S2 and S3 at http://ajp.amjpathol.org) showing the locations of the corresponding boxed regions in A and C indicating the slow migration (B) and the probing movements (D) and of an epithelial DC. Time scale is shown as hh:mm.
