Figure 2.
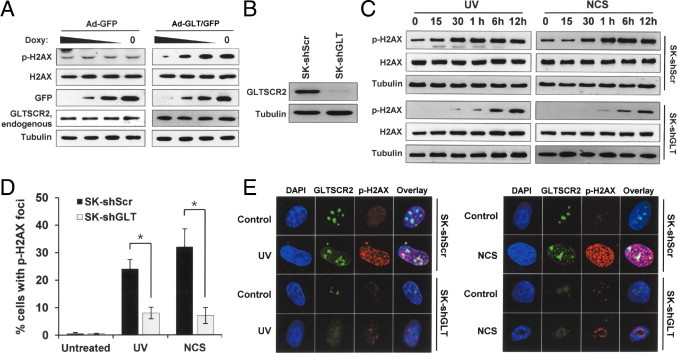
GLTSCR2 is involved in the phosphorylation of H2AX. A: SK-Hep-1 cells were infected by Ad-GFP or Ad-GLT/GFP and incubated in varying concentrations of doxycycline (50, 20, 10 ng/mL) for 24 hours. The resulting protein lysates were then analyzed using Western blot, where anti-H2AX, anti-H2AX, anti-GFP, and anti-GLTSCR2 antibodies were used to detect each target protein. Tubulin was used as the loading control. B: SK-Hep-1 cells were stably infected by either shRNA targeted to GLTSCR2 (SK-shGLT) or scrambled shRNA (SK-shScr), and GLTSCR2 knockdown was assessed using Western blot using an anti-GLTSCR2 antibody. C: SK-shScr and SK-shGLT cells were either exposed to UV (10 J/m2) and harvested at the indicated time points (left) or treated with NCS (50 ng/mL) for the indicated times (right). The resulting cell lysates were then analyzed using Western blot to detect phosphorylated H2AX or the total form of H2AX. Tubulin was used as the loading control. D: SK-shScr or SK-shGLT cells were either untreated or exposed to UV (10 J/m2) or NCS (50 ng/mL). After 12 hours of UV or NCS exposure, the cells were co-immunostained with anti-GLTSCR2 and anti-H2AX antibodies. Next, more than 200 cells were identified so that the number of cells with H2AX nuclear foci formation could be counted by confocal microscopy after nuclear staining with DAPI. For all three independent experiments, data are presented as mean ± SD (*P < 0.01). E: Representative picture of D.
