Figure 1.
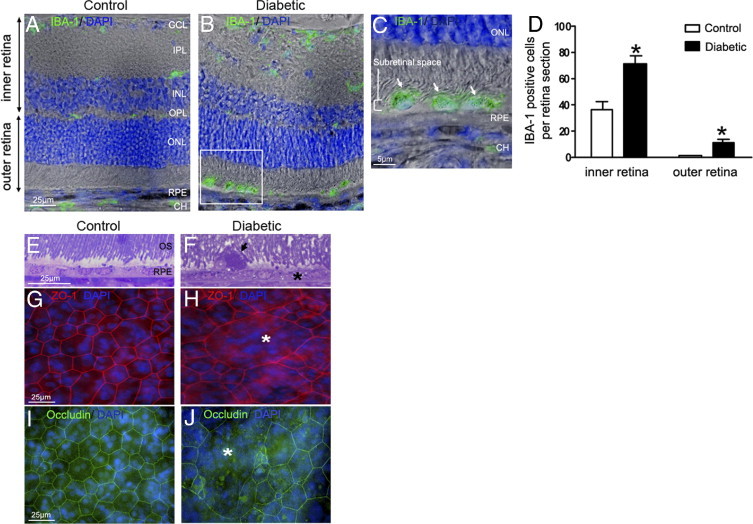
Microglia/macrophages accumulation in the subretinal space of GK rats after 12 months of hyperglycemia. A–C: Retinal sections immunostained with IBA-1 antibody (green) and DAPI (blue) associated with phase contrast. In 12-month-old control rats, IBA-1–positive cells are located exclusively in the inner retina (A). After 12 months of hyperlycemia in GK rats, numerous IBA-1–positive cells are observed in the inner retina and in the subretinal space (B and C; arrowhead and inset). Scale bars: 25 μm (A and B); 5 μm (C). D: Cellular counts of IBA-1–positive cells on cryostat sections of the retina showed a significant increase of their number in the inner retina (1.9-fold) and subretinal space (7.6-fold) in 12-month hyerglycemic rats versus control rats (n = 7 eyes per group). *P < 0.5. E and F: Toluidine blue–stained semithin sections shows vacuolization of RPE cells (asterisk), and presence of a large subretinal cell (arrowhead, F), detected between disorganized outer segments of photoreceptors (OS) in 12-month hyperglycemic GK rats as compared with controls (E). G, H, I, and J: RPE flat mounts stained with Zonula-occludens–1 (ZO-1) (red), occludin (green), and DAPI (blue). In controls, ZO-1 and occludin labeled the regular hexagonal membrane of RPE cells (G and I), whereas in diabetic conditions (12 months of hyperglycemia), we observed some enlarged RPE cells (asterisk) with irrregular ZO-1 and occludin labeling (H and J) showing loss of junctions. Scale bar: 25 μm (A–G). CH = choroid; GCL = ganglion cell layer; INL = inner nuclear layer; IPL = inner plexiform layer; ONL = outer nuclear layer; OPL = outer plexiform layer; OS = outer segment of photoreceptors; RPE = retinal pigmented epithelium.
