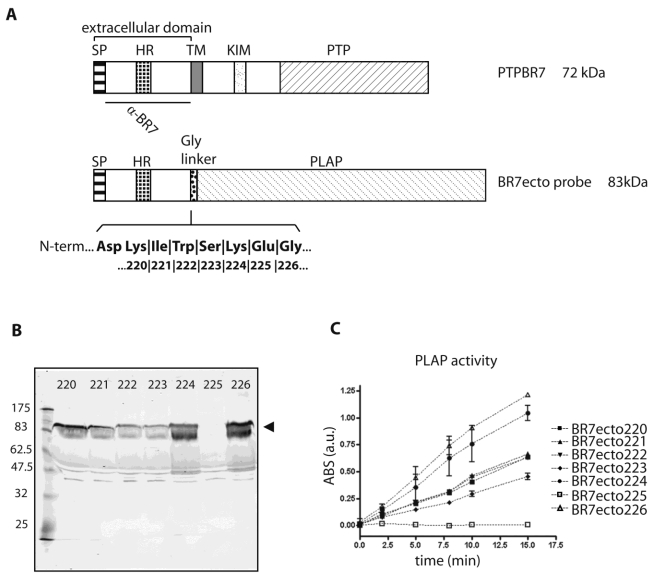
Fig 1.
Characterization of PTPBR7 ectodomain fusion proteins used for RAP in situ assays on mouse brain sections. (A) Schematic representation of mouse PTPBR7 (72 kDa) and the various BR7ecto probes (83 kDa). Signal peptide (SP), hydrophobic (HR) and transmembrane (TM) regions, kinase-interacting motif (KIM), catalytic protein tyrosine phosphatase domain (PTP), flexible Glycine linker (Gly linker), Placental alkaline phosphatase enzyme (PLAP) and the segment recognised by the α-BR7 antiserum are indicated. The seven amino acid residues (position 220, 221, 222, 223, 224, 225 and 226 in PTPBR7) that form the seven different junctions between the extracellular domain and the Glycine linker are highlighted in bold. Resulting probes are named 'BR7ecto' followed by the fusion residue number. (B) Expression and secretion of BR7ecto probes as detected on immunoblots. Conditioned culture media of HEK293T cells transiently transfected with pBG-flexilinker-based expression constructs for the various BR7ecto probes (indicated by the respective fusion residue number on the top of each lane) were subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted using rabbit polyclonal α-BR7 antiserum. The arrowhead points at the position of the BR7ecto probes. Molecular size markers (in kDa) are indicated on the left. (C) Graph reporting the alkaline phosphatase activity within the different BR7ecto probe-containing conditioned media as determined spectrophotometrically using pNPP as a substrate.