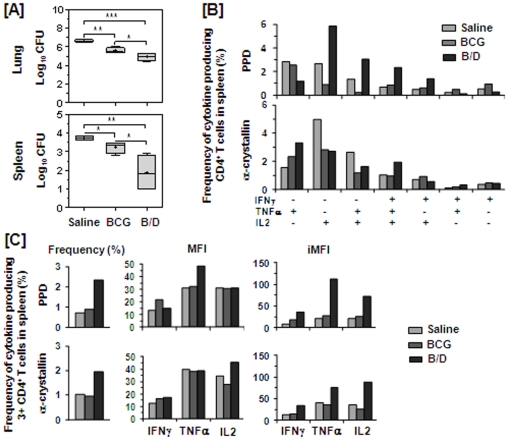
Figure 6. B/D vaccination confers enhanced protection against M. tuberculosis challenge in mice and induces heightened multifunctional CD4 T cell response.
The figure depicts (A) the bacillary load in lungs and spleen of mice (n = 4) at 4 weeks post-infection and (B–C) multifunctional T cell response at 12 weeks post-immunization. Mice experiment was performed once. (A) Log10 CFU is represented by box plot (notations are described in the legend of Fig. 1). The lower limit of detection was 1.0 log10 CFU/g of tissue and animals with undetectable bacilli were allotted a CFU value of 1.0 log10/g. *, p<0.05, **, p<0.01 and ***, p<0.001. (One-way ANOVA). (B–C) T lymphocytes were purified from PPD and α-crystallin stimulated splenocytes (pooled from four mice per group) and stained for CD4 T cell surface marker along with intracellular cytokine staining for IFNγ, TNFα and IL2 followed by FACS analysis. (B) Represents frequency (%) of PPD and α-crystallin specific CD4 T cells expressing each of the seven combinations of IFNγ, TNFα and IL2. (C) Represents frequency of PPD and α-crystallin specific 3+ CD4 T cells along with MFI and iMFI for IFNγ, TNFα and IL2. B/D: BCG prime – DNAacr boost regimen.