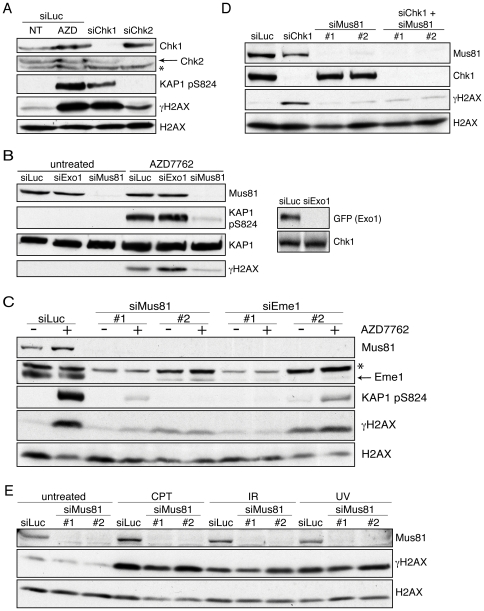
Figure 1. Mus81/Eme1 depletion reduces DNA-damage after Chk1 inhibition.
A. Chk1 inhibition causes DNA damage. Cells were transfected with control siRNA (siLuc) or siRNAs targeting Chk1 or Chk2. siLuc cells were untreated (NT) or treated (AZD) for 5 h with 200 nM AZD7762. * Cross-reacting band. B. Mus81 but not Exo1 is involved in the generation of DNA-damage signals after Chk1 inhibition. Cells were transfected with siLuc, siExo1, or siMus81#1, and treated as in A. Due to an inability to detect endogenous Exo1, the right panel shows depletion of recombinant GFP-Exo1 using the same siRNA. C. Mus81 or Eme1 depletion reduces DNA-damage signals caused by AZD7762 treatment. Cells were transfected with siLuc or with siRNAs targeting Mus81 or Eme1, and treated as in A. * Cross-reacting band. D. Cells were initially transfected with siLuc or siMus81#1 or #2, then 24 h afterwards they were transfected with siChk1 or siLuc. Cells were collected 48 h after the second transfection. E. Mus81 depletion does not reduce γH2AX production after treatment with various DNA-damaging agents. Cells were transfected with siLuc or siMus81 then treated with 1 µM camptothecin (CPT), ionizing radiation (IR, 10 Gy) or ultraviolet light (UV, 10 J/m2), and collected 1 h afterwards.