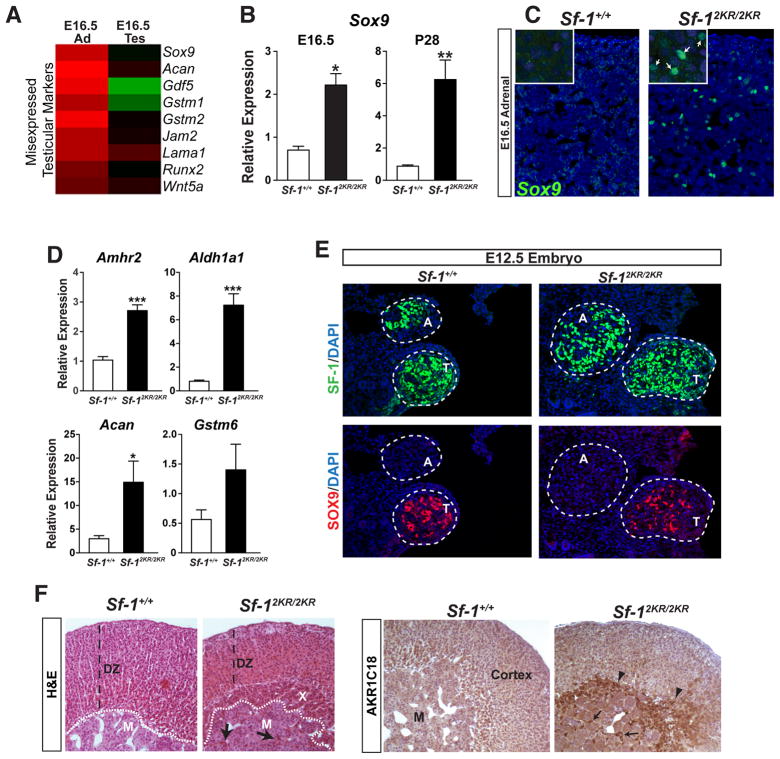
Figure 3. Misexpression of testicular markers such as SOX9, and retention of the fetal X-zone in Sf-12KR/2KR adrenals.
A. Heat map showing upregulated testicular markers in E16.5 mutant adrenals compared to wild type. B. Elevated expression of the testis-specific marker Sox9 in E16.5 and P28 mutant male adrenals. C. SOX9 staining in E16.5 male adrenals (green) in wild type or mutant adrenals (higher magnification shown in inset). D. Expression of testicular markers and Sox9 target genes in E16.5 wild type and mutant adrenals. E. Transverse sections of E12.5 embryos were stained for SF-1 (green) to locate adrenals (A) and testes (T), as indicated by dashed circles. SOX9 (red) signal is absent in adrenals in both wild type and Sf-12KR/2KR embryos. F. Representative photomicrographs of H&E and immunohistochemical staining of 20α-HSD (AKR1C18) in 8-week old male adrenals show cortical hypoplasia and persistence of the fetal X-zone as indicated by AKR1C18 staining (right panel, arrowheads). X-zone infiltration into adrenal medulla is indicated with arrows. DZ, definitive zone; M, adrenal medulla; X, X-zone. See Table S2.