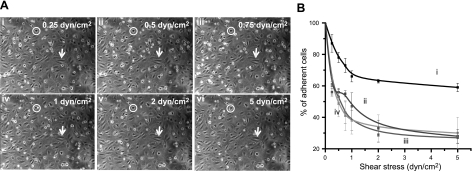
Figure 6.
P-aptamer-MSCs bind to histamine treated HUVECs. A) Representative images demonstrate the accumulation of P-aptamer-MSCs on HUVECs when low to high shear stresses were applied; total number of adhered cells in the same field of view first increases to 0.75 dyn/cm2 and then starts decreasing at higher shear stresses (i.e., 1–5 dyn/cm2). Cell numbers at 0.25 (i), 0.5 (ii), and 0.75 (iii), 1 (iv), 2 (v), and 5 dyn/cm2 (vi) are 54, 63, 76, 55, 50, and 42, respectively. See Supplemental Video S2 for a representative video. Note that perfused circular MSCs (circles) and adherent spindle-shaped HUVECs (arrows) can be easily distinguished by their differing shapes, which was confirmed by immunostaining (Supplemental Fig. 3A, B). B) Percentage of adherent MSCs as a function of shear stress. Only MSCs initially present in the field of view were considered. i) P-aptamer-MSCs. ii) MSCs treated with PBS instead of P-selectin aptamer in the third step of modification. iii) Scrambled sequence-modified MSCs. iv) P-aptamer-MSCs on HUVECs preblocked with P-selectin aptamers.