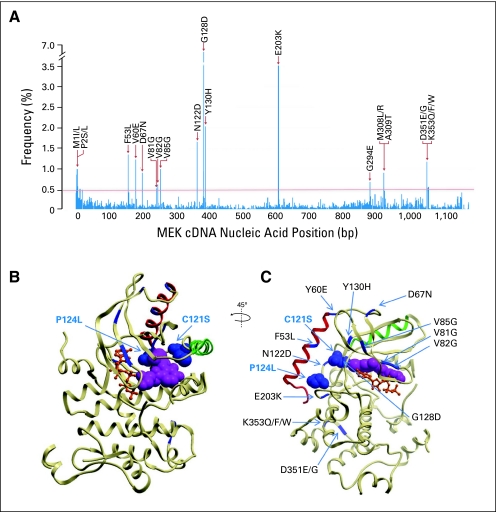
Fig 4.
MEK1 mutations arising from an in vitro mutagenesis screen for resistance to RAF inhibition. (A) Recurrent mutations across the MEK1 coding sequence from a PLX4720 mutagenesis screen (based on approximately 1,000 sequenced clones) are shown. The corresponding amino acid substitutions from high-scoring mutations (> 0.4%) are indicated. (B and C) Locations of selected resistance alleles are indicated within the crystal structure of MEK1. Adenosine triphosphate (orange) and an allosteric, arylamine MEK inhibitor (PD318088; purple) are shown. Helix C (green) and helix A (red) are indicated. Mutations found to confer clinical resistance to RAF inhibition (C121S) and MEK inhibition (P124L) are indicated (blue spheres). Candidate mutations found in the mutagenesis screen are shown in blue. B and C show alternative views of the same crystal structure, with a 45-degree and slight inferior oblique rotation. bp, base pair.