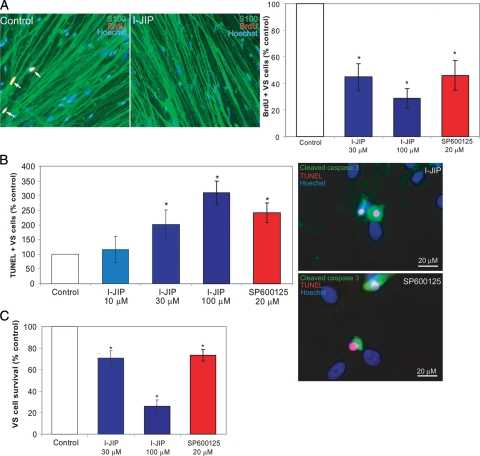
Fig. 6.
c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) activity promotes vestibular schwannoma (VS) cell proliferation and survival. Primary VS cultures were cultured in the presence or absence of JNK inhibitors (I-JIP or SP600125) for 24 h (A and B) or 5 days (C). (A) Representative cultures immunolabeled with anti-BrdU (red) and anti-S100 (green) antibodies. Nuclei were identified with Hoescht 3342 (blue). Arrows indicate BrdU-positive nuclei determined by overlap of red and blue channels. Scale bar = 100 µm. Cell proliferation was determined by scoring the percentage of BrdU-positive, S100-positive VS cells and is expressed as a percentage relative to control cultures, defined as 100%. (B) Apoptosis was scored as the percentage of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL)–positive, S100-positive VS cells with condensed nuclei and is expressed as a percentage relative to control cultures, defined as 100%. VS cultures treated with SP600125 or I-JIP and labeled with TUNEL (red), anti-cleaved caspase 3 antibody (green), and Hoechst (blue) demonstrating activation of caspase 3 in TUNEL-positive cells. Scale bar = 20 µm. (C) VS cell survival, as determined by counting the number of S100-positive cells remaining after 5 days, is expressed as a percentage relative to control cultures, defined as 100%. Error bars represent standard errors of the mean. *P < .05 by 1-way analysis of variance with post-hoc Tukey analysis.