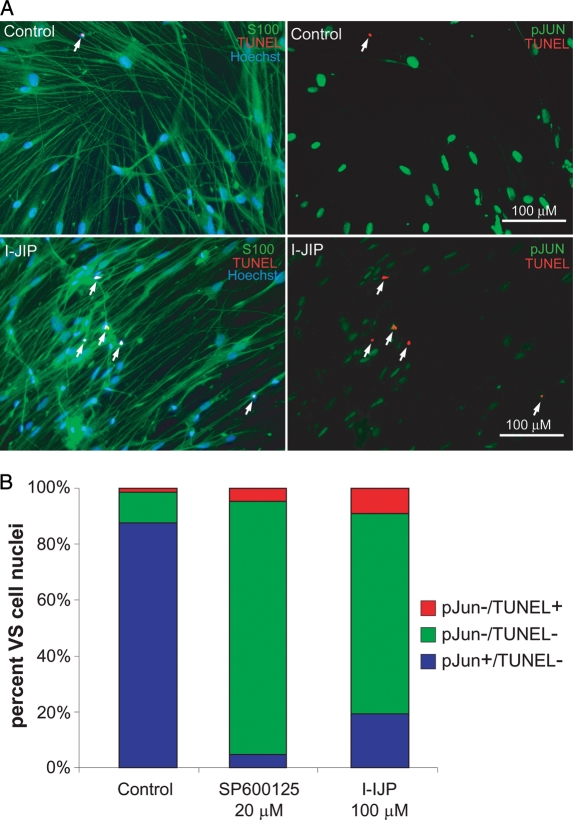
Fig. 7.
Vestibular schwannoma (VS) cell apoptosis due to inhibition of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) correlates with loss of c-JUN phosphorylation (pJUN). VS cultures were treated with JNK inhibitors (I-JIP, 100 µM or SP600125, 20 µM) for 24 h. (A) Representative images of cultures treated with I-JIP and immunostained with anti-pJUN (Alexa 488 secondary antibody, psuedocolored green, right panels) and S100 antibodies (Alexa 647 secondary antibody, psuedocolored green, left panels). Apoptotic cells were detected by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) (red) and nuclei were labeled with Hoechst (blue). Scale bar = 100 µm. (B) The percent of pJUN-negative and TUNEL-positive, pJUN-negative and TUNEL-negative, and pJUN-positive and TUNEL-negative cells were scored. Cells were considered pJUN positive if the ratio of nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio of pJUN immunofluorescence intensity exceeded 5. No cells were simultaneously pJUN positive and TUNEL positive in any condition. At least 300 cells were scored per condition, and the results were repeated in cultures from 3 separate tumors. JNK inhibitors decreased the percentage of pJUN-positive cells and increased the percentage of TUNEL-positive cells.