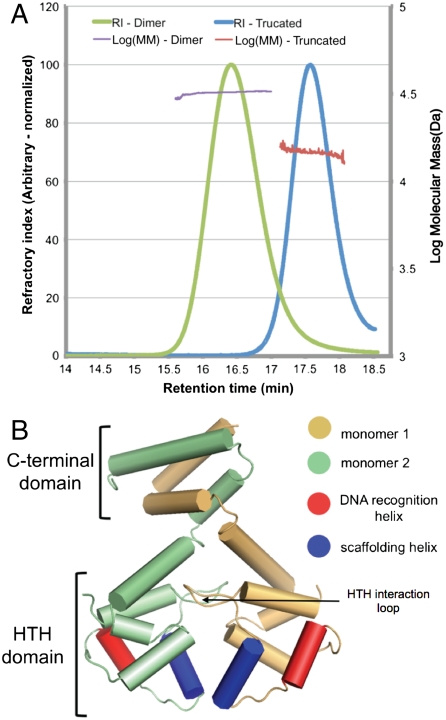
Fig. 1.
The dimeric EspR crystal structure. (A) Full-length (amino acids 1–132) and a truncated form of EspR (amino acids 1–107) from M. tuberculosis were expressed in E. coli, purified, and injected on a Superose 200 gel filtration column. The refractory index (RI) and light scattering (see Materials and Methods) were used to calculate a molecular mass (MM) of 31.8 kDa for the full-length and 15.1 kDa for the truncated EspR. The predicted masses of the full-length EspR monomer and of the truncated form are 14.7 and 12.5 kDa. (B) Schematic of the EspR dimer demonstrating that the two monomers, colored in gold and green, interact at both the C-terminal domain and in the HTH domain. The DNA recognition helix (red) is predicted to fit into the major groove of DNA and the scaffolding helix (blue) is predicted to make additional contacts with the DNA.