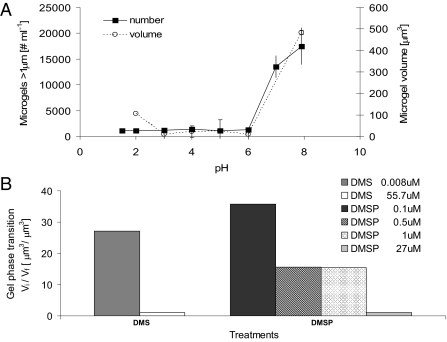
Fig. 2.
Microgel volume phase transition. (A) pH. Marine polymer gels can undergo a fast reversible volume phase transition (<1 min) from a swollen or hydrated phase to a condensed and collapsed phase by changing the pH of the sea water with H2SO4. We then stained the polymer gels with chlortetracycline, monitored the size of the polymer gels by confocal microscopy, and monitored the number of gels by flow cytometry. The swelling/condensation transition is reversible and has a steep sigmoidal change in the volume of the gels. Each data point corresponds to the average and SD of three samples. (B) DMS and DMSP. Marine polymer gels can undergo a fast, reversible change from a swelled/hydrated phase to a condensed phase as a function of DMS and DMSP concentrations, expressed as the ratio between initial (Vi) and final (Vf) microgel volume before and after adding the inducing compound, respectively, and measured with confocal microscopy.