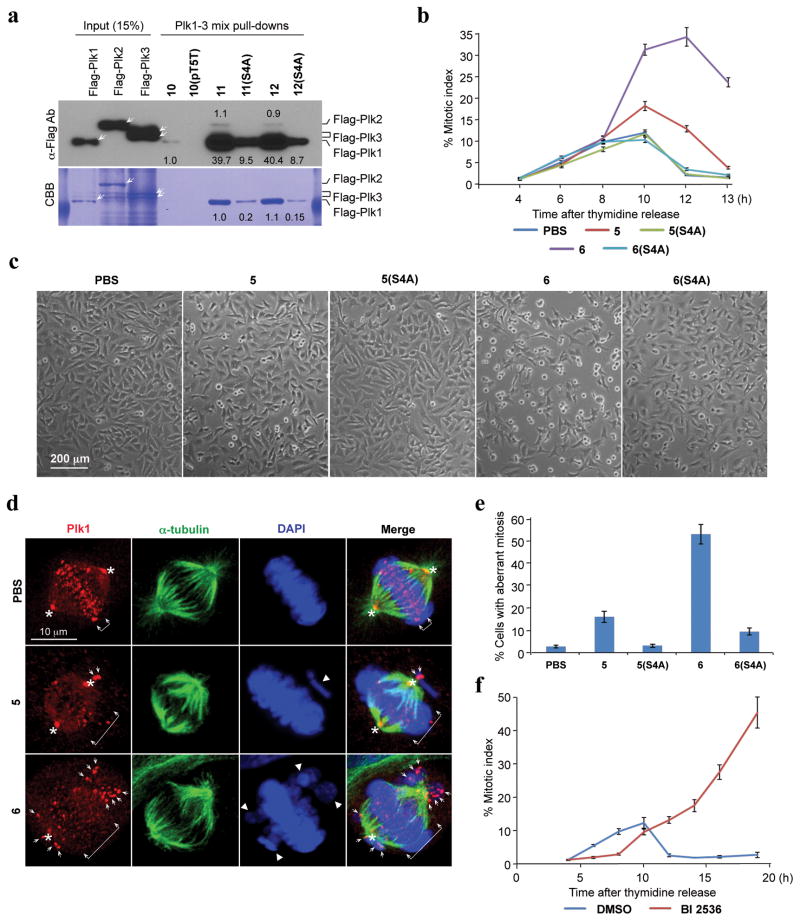
Figure 2.
Specific inhibition of the function of Plk1 PBD by peptide 6. (a) Mitotic 293T cell lysates expressing kinase-inactive Flag-Plk1 (K82M), Flag-Plk2 (K108M), or Flag-Plk3 (K52R) were mixed and incubated with the indicated compounds covalently conjugated to SulfoLink coupling resin through Cys-(CH2)6-CO linker [for 10, 10(pT5T), 11, and 11(S4A)] or an N-terminal Cys residue [for 12 and 12(S4A)]. Precipitates were separated, immunoblotted, and stained with Coomassie (CBB). Arrows indicate Plk1, 2, and 3 proteins. Numbers indicate the relative amounts of precipitated proteins. (b–e). HeLa cells released from a thymidine block and treated with 200 μM of the indicated compounds were quantified to determine the fraction of mitotic cells with rounded-up morphology (b). Bright-field view (c) and fluorescence of immunostained cells (d) used to quantify aberrant mitotic cells with abnormal spindle/DAPI morphologies among total mitotic population (e). Symbols in (d): Asterisks, centrosomally-localized Plk1 signals; arrowed brackets, kineotchore-associated Plk1 signals; arrowheads, misaligned chromosomes. Note that Plk1 signals are almost completely delocalized from the centrosomes and congressed chromosomes, but rather accumulated at the kinetochores of misaligned chromosomes near the poles, as previously described (see48). (f) HeLa cells releasing synchronously from S phase were treated with BI 2536 and analyzed (Supplementary Fig. 14). The data in (b), (e), and (f) represent mean values +/− s.d. (bars) from three independent experiments.