Figure 3.
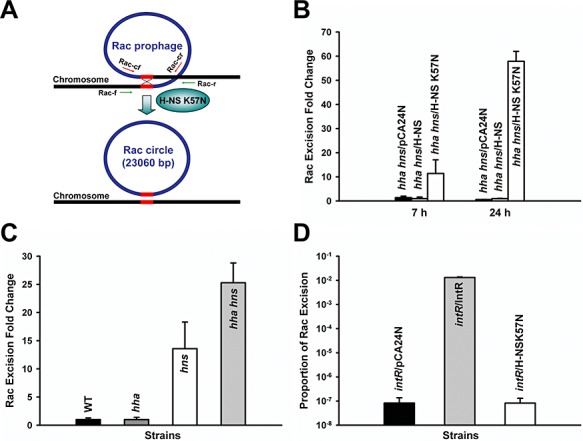
Excision of Rac prophage. Rac prophage in E. coli has two conserved attachment sites (5′‐TTGTTCAGGTTGTATTGTTCTTTCTT‐3′, 26 bp) at the left and the right ends of Rac indicated as red lines (A). Rac excision is induced by H‐NS K57N, and circularized to form a phage‐like circle. Rac excision and phage‐like circle were verified by DNA sequencing using primers Rac up and Rac down (Table S3) and by PCR using primer sets; green arrows indicate primers for Rac excision (Rac‐f and Rac‐r) and red arrows for the Rac circle (Rac‐cf and Rac‐cr) (Table S3). Excision of Rac in LB at 37°C for BW25113 hha hns cells producing H‐NS K57N and wild‐type H‐NS after 7 h and 24 h (B), for BW25113, BW25113 hha, BW25113 hns and BW25113 hha hns without a plasmid after 15 h (C), and for BW25113 intR producing H‐NS K57N and IntR after 24 h (D). The number of chromosomes was quantified by qPCR using a reference gene, purA, using primers purA‐f and purA‐r and the number of chromosomes devoid of Rac was quantified using primers Rac‐f and Rac‐r (Table S3). Each data point is the average of at least four replicates from each of two independent cultures, and one standard deviation is shown. H‐NS K57N, H‐NS and IntR were produced using 1 mM IPTG.
