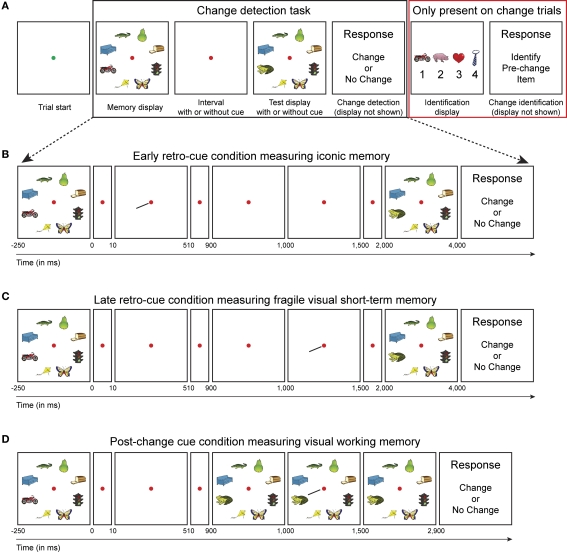
Figure 1.
Experimental design. (A) Subjects performed a change detection task to measure the capacity of short-term memory representations (black box). After each change trial, an identification display was presented that contained the item that was present in the memory display, but not anymore in the match display (so-called pre-change item) in addition to three distracter items that were present in neither memory nor test display (red box). We assume that high-resolution representations support both change detection and identification, whereas low-resolution representations support change detection or pre-change identification only. (B) Early retro-cue condition; 10 ms after off-set of the memory display a spatial cue was presented that singled out the item that changed in 50% of the trials. Effectively, this condition measures iconic memory. (C) Late retro-cue condition; 1 s after off-set of the memory display, but before the on-set of the test display, a spatial cue was presented. Effectively, this condition measures fragile VSTM. (D) Post-change cue condition; 100 ms after on-set of the test display, a spatial cue was presented. This condition measures only visual working memory.