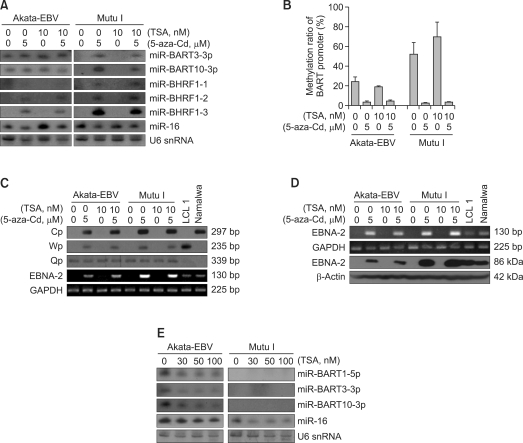
Figure 3.
Effect of 5-aza-Cd and/or TSA on the expression of EBV miRNAs in Akata-EBV and Mutu I cell line. (A) Northern blot for EBV miRNAs was performed using total RNA isolated from the cells treated with 5-aza-Cd (5 µM) and/or TSA (10 nM) for 72 h. (B) Pyrosequencing was carried out for the BART promoter of Akata-EBV and Mutu I cell lines treated with 5-aza-Cd and/or TSA. (C) A specific 3'-primer for each transcript initiating at the Cp, Wp, or Qp was used for cDNA synthesis. cDNA was subjected to latent EBV promoter specific PCR/Southern blot. cDNA of EBNA-2 was also amplified by RT-PCR to confirm latency type. GAPDH mRNA was amplified to compare the quantity and quality of the RNA samples. (D) Expression of EBNA-2 protein was detected using PE2 monoclonal antibody. β-Actin was used as a loading control for Western blot. LCL1 and Namalwa were used as positive controls for the transcripts initiating at Wp and Cp, respectively. (E) Northern blot was performed for BART miRNAs using total RNA isolated from Akata-EBV and Mutu I cells which were treated with TSA (0, 30, 50, or 100 nM) for 24 h. Loading amount of each RNA sample was monitored by reprobing the blot with a specific probe to U6 snRNA. The expression of human miR-16 was assessed as a reference.