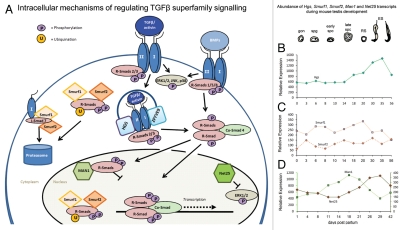
Figure 1.
(A) Intracellular modulators of the SMAD signaling pathway. The binding of a dimeric TGFβ superfamily ligand (e.g., TGFβ, activin or BMP) to its respective type I and type II receptors at the cell surface initiates phosphorylation of R-SMADs (SMAD2 and SMAD3 in the case of activins and TGFβ and SMAD1, SMAD5 and SMAD8 in response to BMPs). Phosphorylated R-SMADs complex with Co-SMAD4, accumulate in the nucleus and, in association with other transcriptional co-regulators, drive or repress target gene expression. TGFβ superfamily members can also activate the mitogen-activated protein kinases ERK1/2, p38 and JNK. SMAD2/3-mediated signaling is enhanced by the endosomal proteins HGS (hepatocyte growth factor-regulated tyrosine kinase substrate) and ZFYVE9 zinc finger FYVE domain containing 9 protein (the murine homologue of human SARA). SMURF1 and SMURF2 are E3 ubiquitin ligases that cause proteosomal degradation of activated receptors (in conjunction with the inhibitory SMAD7) and of SMAD2 and SMAD3, thereby downregulating activin/TGFβ signaling. MAN1 and NET25 localize to the inner nuclear membrane. MAN1 (Lemd3) antagonizes activin/TGFβ/BMP signaling by sequestering SMAD2/3 and SMAD1/5 away from chromatin binding. NET25 (Lemd2) is a truncated form of MAN1 that is unable to bind SMAD proteins but which is a potent inhibitor of mitogen activated protein kinases (MAPKs). Production of one or more of these modulators has the potential to selectively influence the capacity of a cell to respond to one or more TGFβ superfamily ligands. (B–D) Differential expression of genes encoding related TGFβ superfamily signaling modulators during mouse testis development, as determined by Affymetrix microarray. (B) Transcript levels of the endosome-localized HGS, (C) Smurf1 and Smurf2 and (D) Man1 and Net25 exhibit distinct profiles corresponding to progressive changes in the cellular populations throughout the first wave of spermatogenesis. Man1 transcript levels are highest between days 18 and 21, concordant with the prevalence of spermatocytes while Hgs and Net25 levels peak around day 26–35, when round spermatids predominate. Data are compiled from Schultz et al. 2003 and Shima et al. 2004 (Hgs: GDS605; Smurf1 and Smurf2: GDS606; Man1 and Net25: GDS409, available at www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo). Time of first appearance of differentiating germ cell types are depicted above graphs; gon: gonocyte, spg: spermatogonia; early spc: early spermatocytes; late spc: late spermatocytes; RS: round spermatids; ES: elongating spermatids.