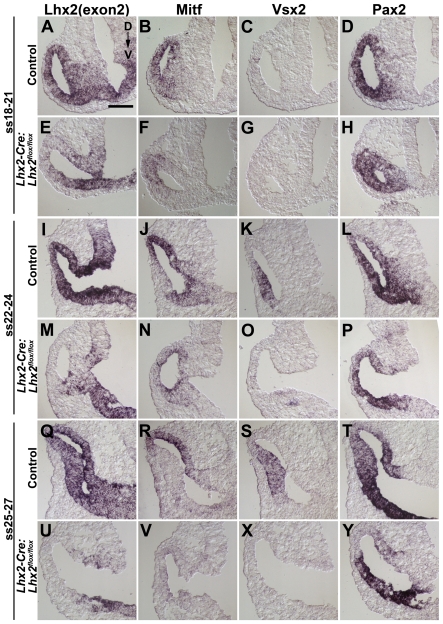
Figure 3. Early patterning of the optic vesicle is initiated following conditional inactivation of Lhx2 in the eye-committed progenitor cells.
(A–Y) In situ hybridisation analyses of coronal sections of the optic vesicles in control and mutant (Lhx2-Cre:Lhx2flox/flox) embryos at the indicated developmental stages. A,E,I,M,Q,U are in situ hybridisation analyses to detect exon 2 (exon2) in the Lhx2 mRNA to reveal the domain in the optic vesicle where the Lhx2 gene has been inactivated. B,F,J,N,R,V are in situ hybridisation analyses to detect expression of the RPE cell-specific gene Mitf, which is expressed in the entire optic vesicle in early development and eventually becomes RPE cell-specific. C,G,K,O,S,X are in situ hybridisation analyses to detect expression of neural retina specific gene Vsx2. D,H,L,P,T,Y are in situ hybridisation analyses to detect expression of the optic stalk-specific gene Pax2. Dorsal to Ventral orientation for all sections is indicated in A. Scale bar: 100 µm.