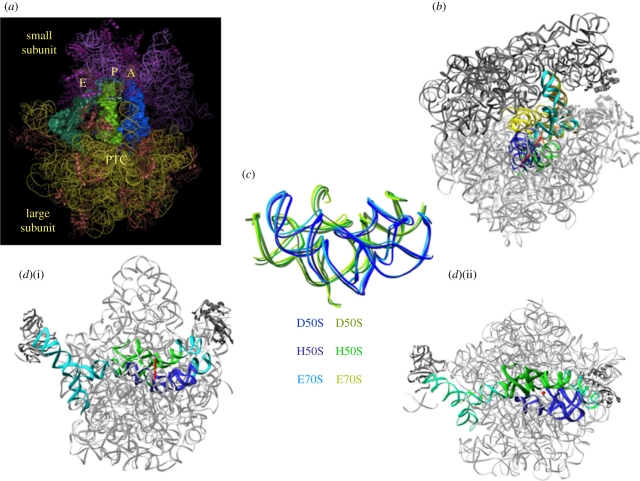
Figure 1.
The ribosomal symmetrical region. In all panels, the ribosomal RNA is shown in grey. The blue and green ribbons indicate the ribo-phosphate ester backbones of the rRNA of the A- and the P-regions of the symmetrical region. The red rod indicates the position of the imaginary axis and the red dot indicates a section cut parallel to the direction of the symmetry axis. (a) An overall representation of the ribosome with its three tRNA substrates and the location of the peptidyl transferase centre (PTC). (b) The position of the symmetrical region within the entire ribosome, with A- and P-site tRNAs (cyan and brown, respectively), and the intersubunit bridge that connects between the rims of the cavity leading to the PTC and the decoding centre. (c) The universality of the symmetrical region is indicated by the superposition of the pocket suggested to represent the remnant of the proto-ribosome as in the large subunits from the eubacteria Deinococcus radiodurans, D50S (PDB accession code 1NJP), the archaeon Haloarcula marismortui, H50S (PDB accession code 1VQN) and the entire ribosome from Escherichia coli E70S (PDB accession code 2AVY). (d) Two views (i) and (ii) of the symmetrical region and its non-symmetrical extensions (in cyan) within the contemporary ribosome, which connect all ribosomal functional regions.