Figure 1. Identifying neuronal types in cell culture.
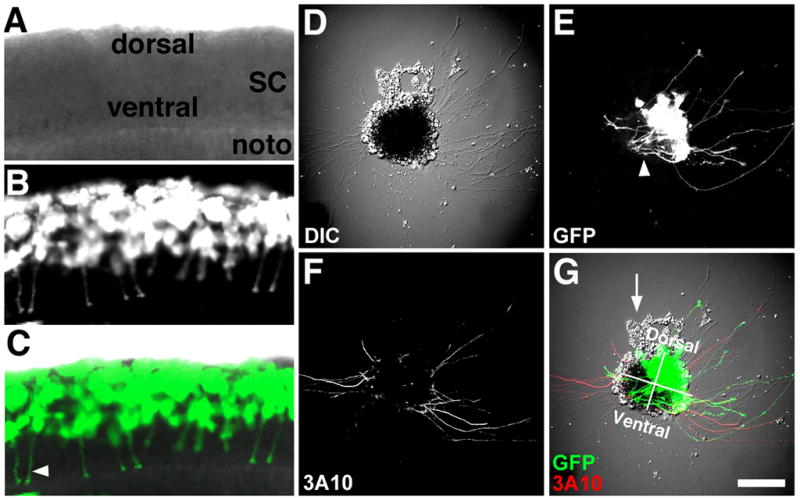
A–C. Confocal microscope images of a ~24 hpf live Xenopus embryo that was previously injected at the 8-cell stage with mRNA encoding GFP into a single blastomere fated to make dorsal spinal cord. Note many ventrally projecting CIs (commissural interneurons; arrowhead in C). D. DIC image of a spinal cord explant in cross-section from the same spinal cord as in (A–C) cultured onto PDL-LN coverslips for 24 hrs. E. GFP fluorescence shows many labeled RB (Rohon-Beard) and CIs extending from the dorsal-lateral region of this explant. Also note many presumed CIs that extend toward the floor plate and stay within the explant (arrowhead). F. Fixed explant that was immunofluorescently labelled with an anti-neurofilament antibody (3A10) that is specific for CIs and the peripheral process of RB neurons in vivo. Note dorsal lateral labeled axons emerge from both sides of spinal explant G. Merged image of fluorescent and DIC channels with dorsal-ventral and right-left quadrants indicated. Presumed neural crest cells (arrow) are often observed migrating from the dorsal aspect of spinal cord explants. Scale bar, 62 μm (in A-C) and 100 μm (in D–E).
