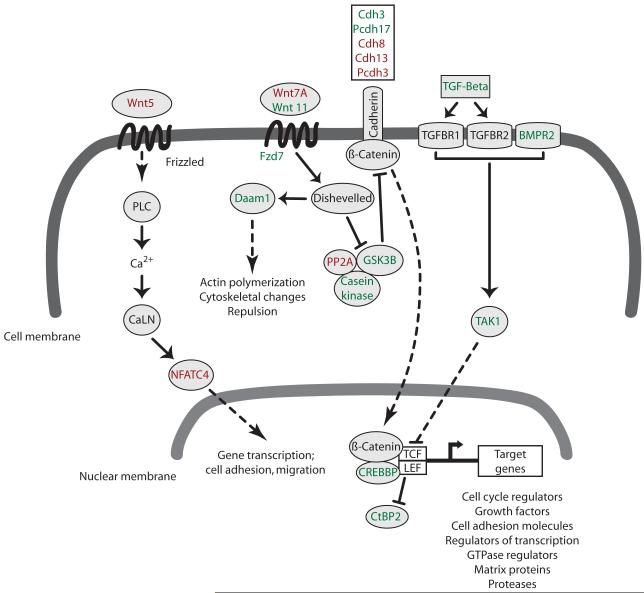
Figure 6. Schematic representation of cocaine-induced amygdalar gene changes in the Wnt pathway.
Adolescent cocaine exposure regulated the mRNA expression of many genes involved in Wnt signaling pathways. These signaling pathways can alter the morphology of the actin cytoskeleton and participate in the remodeling of synaptic and dendritic structures following exposure to drugs of abuse. Signaling by Wnt molecules leads to the activation of transcription factors and target genes. In the canonical Wnt pathway, dishevelled inhibits a kinase-associated scaffolding complex (GSK3B, casein kinase, PP2A) that normally facilitates the degradation of beta catenin. Free beta catenin translocates to the nucleus where it activates the transcription of Wnt target genes. Dishevelled, as well as axon guidance molecules, also induce changes in actin polymerization and cytoskeletal proteins via the activation of Rho GTPases. The calcium-mediated Wnt signaling pathway is controlled by the Wnt5 molecules and activates transcription of cell surface proteins and cell adhesion molecules. Shown in green are upregulated genes and shown in red are downregulated genes. Solid arrows show direct interactions and dashed arrows denote signaling processes with intermediates not shown. Abbreviations: CaLN, calmodulin; LEF, lymphoid enhanced binding factor; PLC, phospholipase C; TAK1, Tgf beta activated kinase 1; TCF, t-cell transcription factor; TGFBR1/2, transforming growth factor beta receptor 1/2. For a detailed list of all other genes names see table 3.