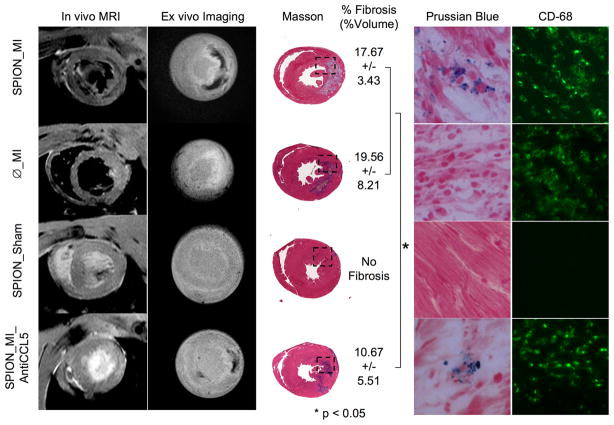
Figure 2.
In vivo and ex vivo imaging of monocytes at day 3 post-MI labeled using iron oxide nanoparticles 3 days before MI and its comparison with all groups at Day 3. SPION_MI clearly showed a hypointense signal by magnetic resonance imaging (in vivo and ex vivo) in the myocardial infarction. The fibrosis of this group was calculated to 17.67+3.43% (%vol). There were numerous fluorescent-loaded cells in the myocardial infarction, corresponding to CD68-positive cells. Ø_MI did not show hypointense signal by magnetic resonance imaging, or iron-loaded cells by histology. The fibrosis was 19.56+8.21%. The SPION_Sham group did not show an inflammatory infiltrate or myocardial infarction. The SPION_MI_AntiCCL5 showed a hypointense signal by magnetic resonance imaging, smaller fibrosis (10.67+5.51%) and less iron-loaded CD68-positive cells in the myocardial infarction. *P < 0.05. (Reprinted from Montet-Abou K, Daire JL, Hyacinthe JN et al. In vivo labelling of resting monocytes in the reticuloendothelial system with fluorescent iron oxide nanoparticles prior to injury reveals that they are mobilized to infarcted myocardium. European Heart Journal 2010 June; 31(11):1410-20, by permission of Oxford University Press.)