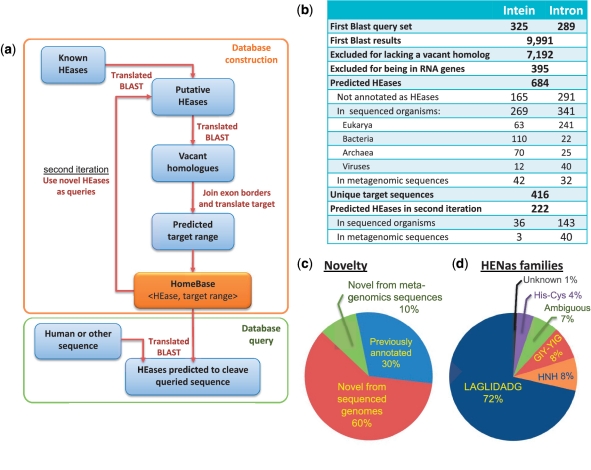
Figure 3.
The HomeBase algorithm and database. (a) Database construction involves: (i) the identification of putative HEGs in both genomic and meta-genomic databanks using translated BLAST searches; (ii) The identification of vacant homologs using a second translated BLAST; (iii) The identification of exon boundaries and the prediction of the target based on the vacant homologs and the translation of the target to define the target range. The HomeBase database consists of a set of HEG sequences and the predicted target range of each HEase. The user may then query HomeBase with (e.g.) a human gene of interest and receive a list of HEases, which are predicted to cleave the query sequence based on a translated BLAST search against the targets in the database. (b) Statistics of the HomeBase database. (c) A pie diagram depicting the percentage of previously annotated versus newly discovered HEGs within the results of the HomeBase algorithm. (d) Classification of HomeBase HEGs into structural families.