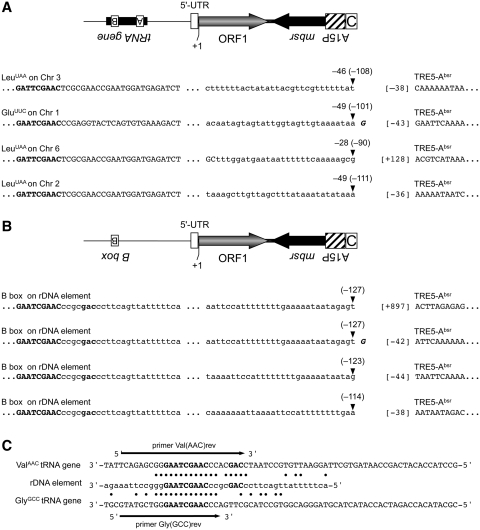
Figure 7.
De novo integration sites for TRE5-Absr elements. Examples of integration sites upstream of tRNA genes on four different D. discoideum chromosomes (A) and four independent integration events into the same position on the extrachromosomal rDNA element (B). Element 8 was allowed to amplify, bsrR clones were pooled and integrants were isolated by PCR on genomic DNA using tRNA gene family-specific forward primers and an mbsrI-specific reverse primer. PCR fragments were cloned and sequenced. Indicated in bold letters is the B box sequence of the isolated tRNA gene. The distances from the integrated TRE5-Absr element to the first nucleotide of the tRNA gene are indicated by negative numbers (e.g. –46). The corresponding distances to the B boxes of the targeted tRNA genes are provided in round brackets (e.g. –108). The first nucleotides of the integrated TRE5-Absr elements are indicated by numbers in square brackets left to the TRE5-Absr sequence. The +1 nt of the TRE5-Absr element was defined as the start of translation for ORF1, meaning that ‘[–38]’ refers to the 5′-UTR derived from the actin6 promoter. (C) Similarity of tRNA gene-specific primers with sequences on the rDNA element. Shown are the complete sequences of the D. discoideum ValAAC and GlyGCC tRNA genes. Note that the DNA sequences are written in the same orientation as in panel B. The B boxes are written in bold. A section of the rDNA element is shown with black dots indicating sequence identities to the two tRNA genes. The arrows indicate the tRNA-specific primers used to search for TRE5-Absr integrations in the D. discoideum genome.