Figure 3.
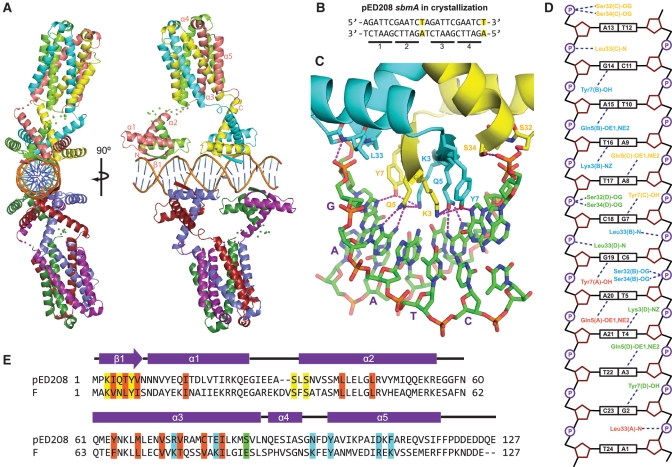
Crystal structure of pED208 TraM bound to sbmA. (A) Orthogonal views of the overall structure of the TraM–sbmA complex. The α-helices and β-strands are indicated. Disordered linkers are indicated by spheres, one for each Cα that could not be refined. (B) sbmA sequence used for crystallization. Mutated residues are highlighted. GANTC TraM-binding motifs are underlined and numbered. (C) Interactions between the N-terminal domain of TraM and DNA. Hydrogen bonds are indicated by purple-dashed lines. The GAATC-binding motif consisting of bases G7 to T11 of sbmA is indicated with purple letters. (D) Schematic diagram of TraM–sbmA interactions for one TraM tetramer. Hydrogen bonds are indicated with dashed lines. (E) Sequence alignment of pED208 TraM and F TraM. Secondary-structure elements are indicated. Conserved hydrophobic core residues are highlighted in orange, DNA-contacting residues in yellow, TraD C-terminal tail-contacting residues in cyan and position 88, responsible for protonation-mediated destabilization of the F TraM tetramer, in green.