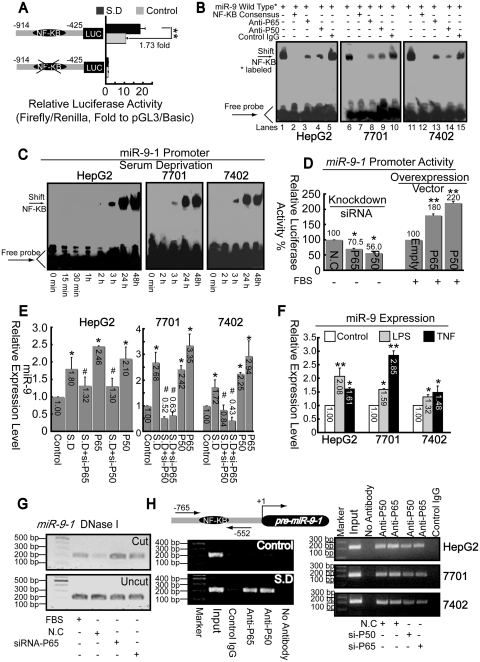
Figure 6.
P50/P65 mediates up-regulation of miR-9 via interaction with pri-miR-9-1 promoter. (A) Promoter activities of fragment from −914 to −425 relative to pre-miR-9-1 with or without putative κB motif were detected before and after SD in HepG2 cells. **P < 0.01. (B) Nuclear extracts from cells 1 day after SD were assayed by EMSA using biotin-labeled oligonucleotide probes (from −700 to −673) and NF-κB consensus probes. Shifted bands were verified by addition of 5 μg either non-specific control IgG or specific antibodies against P65 or P50, as indicated. (C) EMSA assays were performed using nuclear extracts from three hepatoma cell lines after SD for indicated time and wild-type probes (from −700 to −673). (D) Promoter activities from miR-9-1 reporter were measured after overexpression of NF-κB components, as indicated, with FBS condition or knockdown either P65 or P50 using specific siRNA under SD. *P < 0.05, and **P < 0.01 versus the control (NC or empty). (E) Total RNA from cells was extracted after treatment with siRNA or pcDNA3.1 vector targeting either P50 or P65. Then miR-9 levels were measured using real-time PCR. *P < 0.05, versus the control and #P < 0.05 versus the SD. (F) Effects of LPS or TNFα on miR-9 expression. *P < 0.05, and **P < 0.01 versus the control. (G) Open-chromatin-accessibility status around the κB motif under different treatment as indicated in HepG2 cells was measured via Chart-PCR (31 reaction cycles) using DNase I by same primer sets used in Figure 6H. (H) ChIP analysis was performed to qualitatively confirm the interaction of NF-κB components, P50 and P65 with the miR-9-1 promoter in vivo (left panel). Right panel, in vivo interactions of NF-κB with pri-miR-9-1 promoter after SD upon suppression of P50/P65 protein by specific siRNA were determined by ChIP assay again.