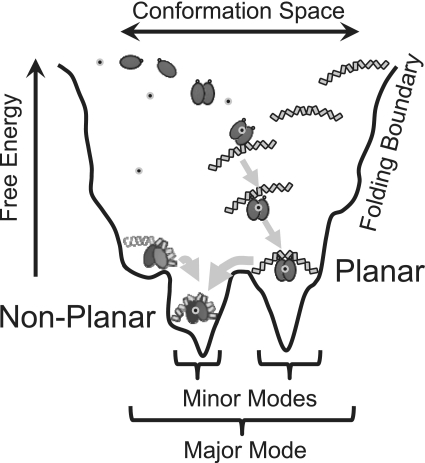
Figure 5.
Schematic folding funnel for SyCrp1 conformational selection with linear B-form DNA substrates in vitro. Planar (class II) dyad and non-planar dyad (+13)bend or non-planar (+)monad (+13)bend conformers are represented as in Figure 2. The cAMP molecule is represented with small grey circled black dots. In this model, SyCrp1 cAMP-independent binding has not yet been rejected, but has been rejected for EcCrp due to cAMP-dependent induced fit changes to the C-helix secondary structure. Attaining a bound state is dynamic in this model. SyCrp1 must exhibit conformational entropy (61) leading to conformational-capture (33) because the DNA sequence determines the sequential minor mode folding paths (arrows) leading to the lowest energy conformer. In vivo DNA topology landscapes impose additional influences due to imposed supercoiling and flanking chromatin.