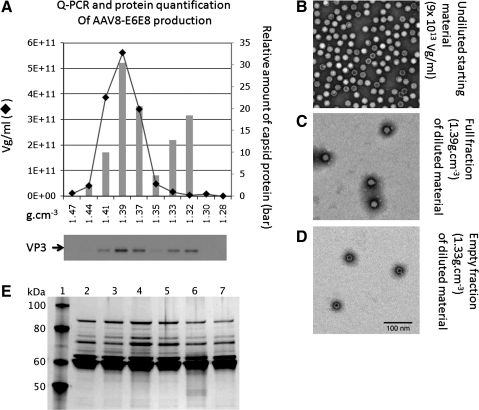
FIG. 6.
Physical vector characterization. (A) Following CsCl isopycnic centrifugation, gradients were fractionated and assayed for the presence of capsid protein and vector DNA. The graph represents the DNA content of each fraction (solid line), and the columns indicate the relative amount of capsid protein in each fraction. The signal from each fraction was divided by total VP3 signal on the western blot (lower panel). The abscissa denotes the density of each fraction in g/cm3. The ordinates represent the DNA content, as vg/ml (left axis) and relative VP3 amount in each fraction (right axis). The buoyant density of empty particles is approximately 1.32 g/cm3 and that of filled particles is 1.39 g/cm3. Based on the distribution of vector DNA and protein across the gradient, approximately 65% of the capsids contain vector DNA. (B–D) TEM images of rAAV particles. Negatively stained rAAV particles from unfractionated material (B) and high- (C) and low-buoyant (D) density fractions are consistent with the ratio of full and empty particles described in (A). In the unfractionated, undiluted starting material (C), >50% of the particles appear full. (E) Silver-stained polyacrylamide gel of rAAV proteins following IA chromatography and TFF concentration/diafiltration. An aliquot (0.5 μl) of each vector was fractionated by SDS-PAGE, and proteins were visualized by silver staining. The rAAV6-AlkPhos production yielded 1.94 × 1016 vg from approximately 200 L. The samples and concentrations are listed. Lane 1, molecular mass standards; lane 2, rAAV6-U7smOPT (9 × 1013 vg/ml); lane 3, rAAV6-U7smOPT (5.77 × 1013 vg/ml); lane 4, rAAV6-AlkPhos (5.18 × 1013 vg/ml); lane 5, rAAV6-U7smOPT (7 × 1013 vg/ml); lane 6, rAAV6-U7smOPT (9 × 1013 vg/ml); lane 7, rAAV6-GFP (6.7 × 1013 vg/ml).