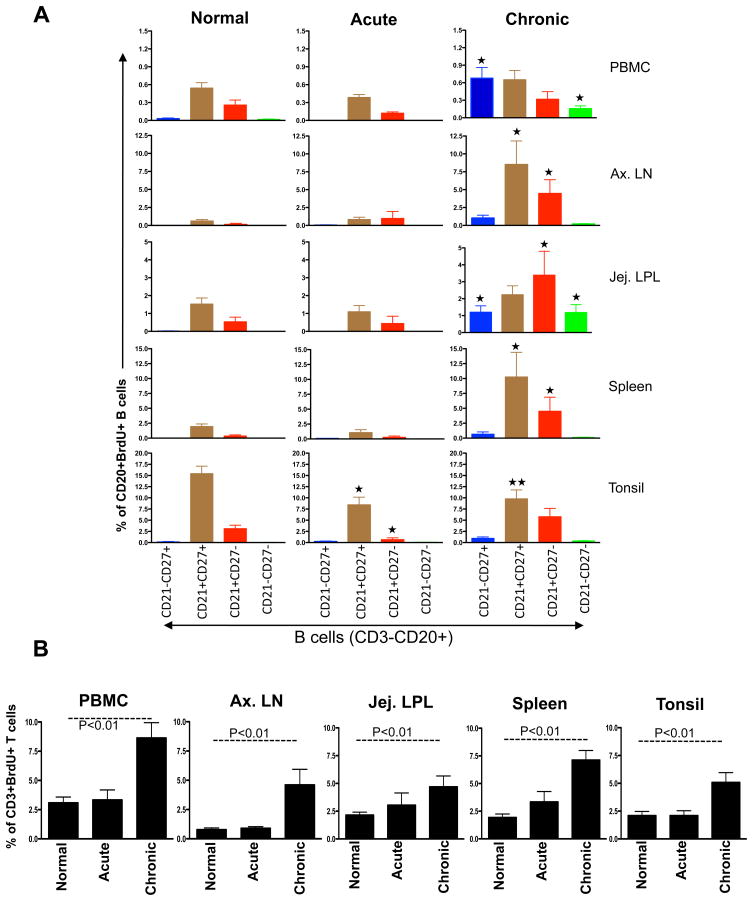
Figure 2.
Bar graphs showing the mean BrdU+ proliferative responses in different CD20+ B cell subsets (A) and CD3+ T cells (B) from different tissues of normal and SIV infected macaques in acute and chronic infection. BrdU was injected intraperitoneally and tissues were collected 24 hrs after inoculation. (A) Higher proliferation of CD21+CD27+ B cell subsets compared to other B cells subsets were observed in all healthy normal rhesus macaques. Interestingly tonsillar CD21+CD27+ B cell proliferation decrease in both acute and chronic SIV infection compared to normal healthy macaques.
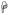 (p<0.01) and
(p<0.01) and
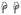 (p<0.05) indicate significant differences between the specified cell subsets and the same subset from normal groups. (B) A significant increase in T cell proliferation in chronically infected RMs compared to acutely infected and normal RMs in all tissues was detected.
(p<0.05) indicate significant differences between the specified cell subsets and the same subset from normal groups. (B) A significant increase in T cell proliferation in chronically infected RMs compared to acutely infected and normal RMs in all tissues was detected.