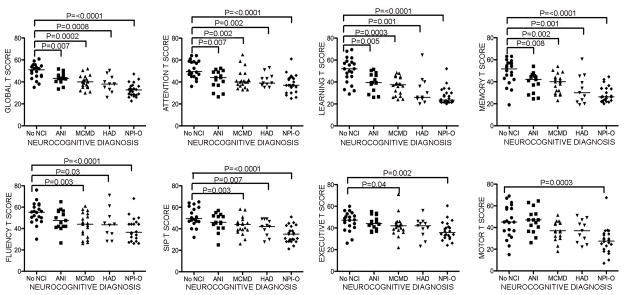
Figure 2. Higher plasma sCD14 levels are associated with global T scores indicating neurocognitive impairment.
Subjects were grouped by global T <40 or ≥40 to compare biomarker levels. Only plasma sCD14 levels were significantly different between subjects with versus without impaired global T scores (second row, first panel), and correlated negatively with global T scores (second row, last panel). (VL, viral load). Median values are indicated as horizontal lines. Statistical significance between groups was calculated using the two-tailed Mann-Whitney test, and significance among continuous variables was calculated using Spearman rho correlation; significant differences (p<0.05) are indicated.