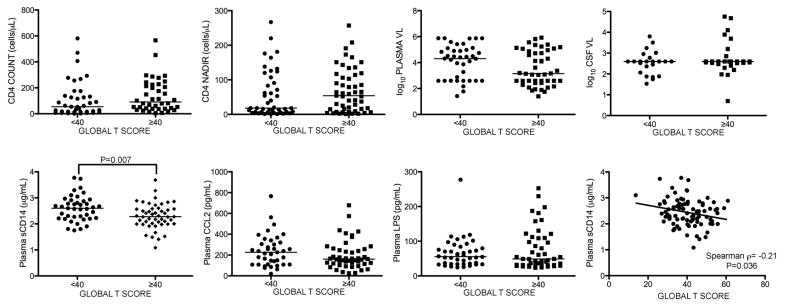
Figure 3. Higher plasma sCD14 levels are associated with impaired test performance in attention and learning domains.
Plasma levels of sCD14, CD4 count, and plasma VL were compared to domain T scores in subjects grouped by T scores <40 or ≥40. A. Plasma sCD14 levels were elevated in subjects with attention and learning T scores <40, B. Lower CD4 counts in subjects with fluency and motor T scores <40. C. Higher plasma VL in subjects with motor T scores <40. D. Plasma sCD14 correlated negatively with attention and learning T scores, and plasma VL correlated negatively with motor T scores. (VL, viral load). Median values are indicated as horizontal lines. Statistical significance between groups was calculated using the two-tailed Mann-Whitney test, and correlations between continuous variables were analyzed using Spearman rho correlation; significant differences (p<0.05) are indicated.