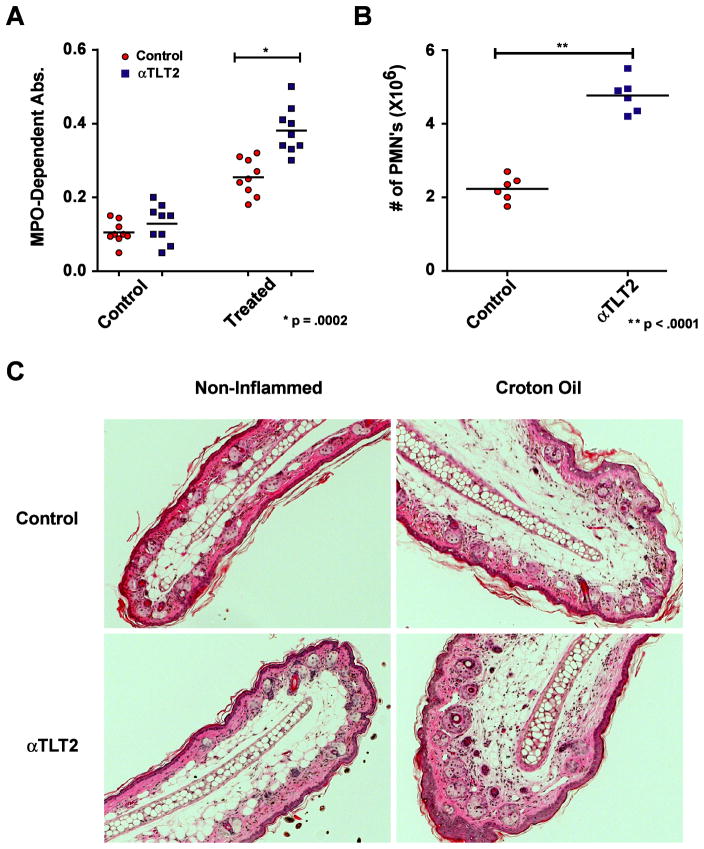
Figure 5. Administration ofαTLT2 mAb results in enhanced accumulation of neutrophils at sites of inflammationin vivo .
Either 100 μg of the αTLT2 mAb 1H4 or an equivalent volume of PBS was administered to groups of mice via i.v. injection. After 30 min, a solution of 2% Croton Oil in acetone was applied to the pinna of one ear, whereas only acetone was applied to the other (control ear). After 4 h, the mice were sacrificed and a 4 mm biopsy was removed from the center of the ears using a biopsy punch. These samples were homogenized and assayed for MPO activity using the colorimetric substrate TMB. The measured absorbance values are depicted for αTLT2 mAb treated and control mice for both ears (A). To determine the number of neutrophils recruited, lysates from known numbers of purified neutrophils were compared to serial dilutions of HRP to develop a standard curve. Using this standard curve for the MPO dependent conversion of TMB, the numbers of neutrophils present in the Croton Oil treated ears for αTLT2 mAb treated and control mice were calculated (B). The data presented represent a minimum of 5 mice and the mean ± SD, and significant p values are shown for both (A) and (B). (C) H & E staining of ear sections taken at 3 h from mice injected with saline (control) or αTLT2 mAb. Representative sections are shown for both control ears that were treated with acetone alone as well as inflamed ears treated with croton oil in acetone. The sections are representative of at least three independent experiments.