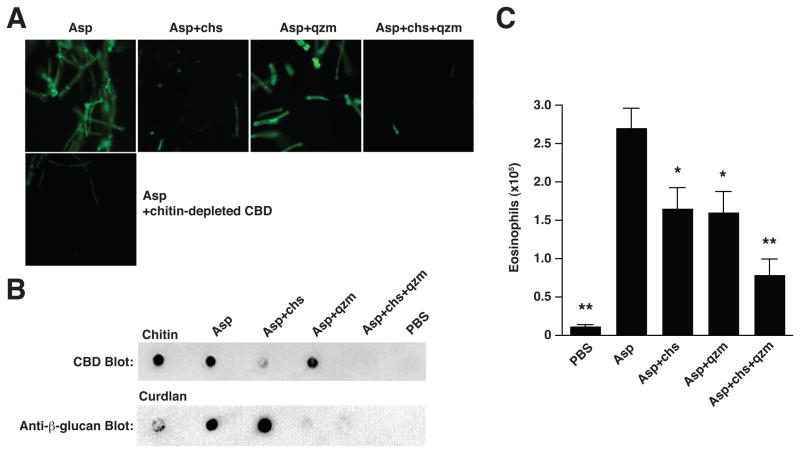
Figure 4. Fungal-induced eosinophil accumulation is attenuated by enzymatic degradation of chitin and β-glucans.
(A) Reactivity of FITC-conjugated chitin-binding domain (CBD) with A. niger preparation (Asp) before and after digestion with chitinase (chs) and/or β-glucanase (Quantazyme; qzm). Lower panel, Asp reactivity with CBD-FITC that was pre-incubated with chitin. Magnification, 20x. (B) Dot-blot assay indicating the presence of chitin (top) or β-glucans (bottom) before and after enzymatic treatment. (C) Numbers of total lung eosinophils 1 day after 2 intranasal Asp challenges, with or without prior enzymatic treatment as indicated. Total live eosinophil numbers were calculated from flow cytometry percentages as described in Figure 2. Mean±SEM, n=8–10/group; *p<0.01, **p<0.001, significantly different from Asp, unpaired t-test.