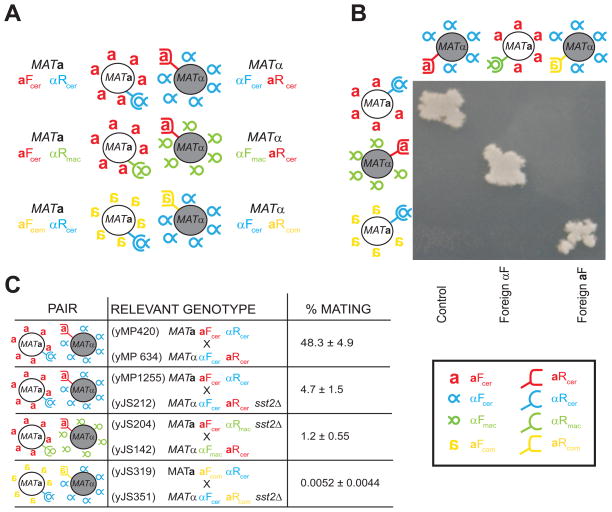
Figure 2. Cells expressing heterologous pheromone-receptor pairs can mate.
A) Mating pairs that conserve the asymmetry between a-factor-like and α-factor-like pheromones. First line: Control mating relying on S. cerevisiae pheromones (aFcer (red a) αRcer (blue α)) and receptors (aRcer (red U-shaped receptor) αFcer (blue semi-circular receptor)). Second line. MATa cells expressing the α-like receptor from S. macrospora (αRmac, green semi-circular receptor) were mated to MATα cells expressing the S. macrospora α-factor-like peptide (αFmac, inverted green α). This pair communicates via the α-factor from S. macrospora and the a-factor from S. cerevisiae (aFcer, red a). Third line: MATa cells expressing an a-factor-like pheromone from S. commune (aFcom, yellow inverted a) were mated with MATα cells expressing the corresponding S. commune receptor (aRcom yellow U-shaped receptor). This pair communicates via the a-factor from S. commune and the α-factor from S. cerevisiae. B) Visualizing mating with heterologous pheromone-receptor pairs. The cells described in A) were streaked, replica plated on top of each other, and allowed to mate over night in complete media. They were then replica plated onto media where only diploids could grow. The absence of off-diagonal mating shows that only strains expressing complementary pheromones and receptor pairs can mate. C) Quantitative mating data. The indicated crosses were allowed to mate on filters for 4 hours (for the cross using two homologous receptor-pheromone pairs) or for 7h (in the case of the sst2Δ and heterologous crosses). Filters were then washed and cells plated on selective media to select for diploids. Mating efficiency is calculated as described in the Materials and Methods. Errors are standard deviations from at least three independent mating trials. Note that the aFcom producing strains (yJS319, last row) were mixed in an excess of 5:1 with the other partner in the mating. All the other crosses were done at a 1:1 ratio. Legend: Red: a-factor (aFcer) and a-factor (aRcer) receptor from S. cerevisiae. Blue: α-factor (αFcer) and α-factor receptor (αRcer) from S. cerevisiae. Green: α-factor (αFmac) and α-factor receptor (αRmac) from S. macrospora. Yellow: a-factor (aFcom) and a-factor receptor (aRcom) from S. commune.