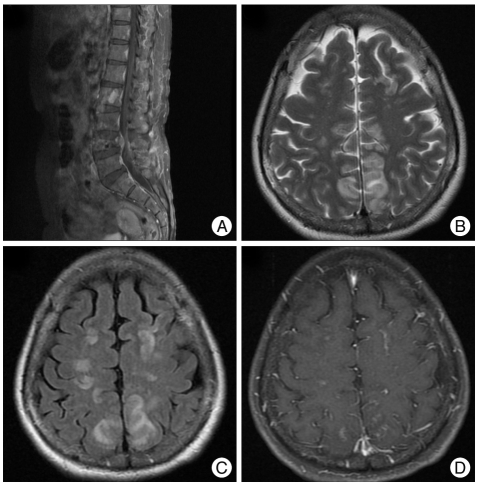
Fig. 1.
Computed tomography and magnetic resonance (MR) imaging at the time of the seizure attack. A metastatic tumor with an epidural extension is detected at the 4th lumbar vertebra in a gadolinium enhanced T1-weighted sagittal image (A). At the time of the seizure attack, there was no abnormality in the computed tomography. Magnetic resonance imaging was taken one day later. An increased signal intensity is detected in the cortex and the subcortical white matter of the parieto-occipital lobe in the T2-weighted axial image (B) and the fluid-attenuated inversion recovery MR imaging (C). This lesion shows a focal enhancement in the gadolinium enhanced T1-weighted axial image (D). There waiss no restriction of diffusion in the diffusion-weighted MR imaging. The MR angiography reveals no vascular abnormalities.